
Font_Awesome_5_brands_npm by Font Awesome is licensed under CC

Font_Awesome_5_brands_npm by Font Awesome is licensed under CC
When a function is called, the computer must "remember" the place it was called from... so that it can return to that location with the result once the call is complete. Typically, this information is saved on the call stack... For tail calls, there is no need to remember the caller...
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tail_call
Some interpreters (and compilers) eliminate the stack frame creation and destruction work when they recognize tail recursion.
Create a folder for the *new* node module.
$ mkdir haddley-factorial-js
Navigate to the new folder
$ cd haddley-factorial-js
Create a package.json file
$ npm init -y
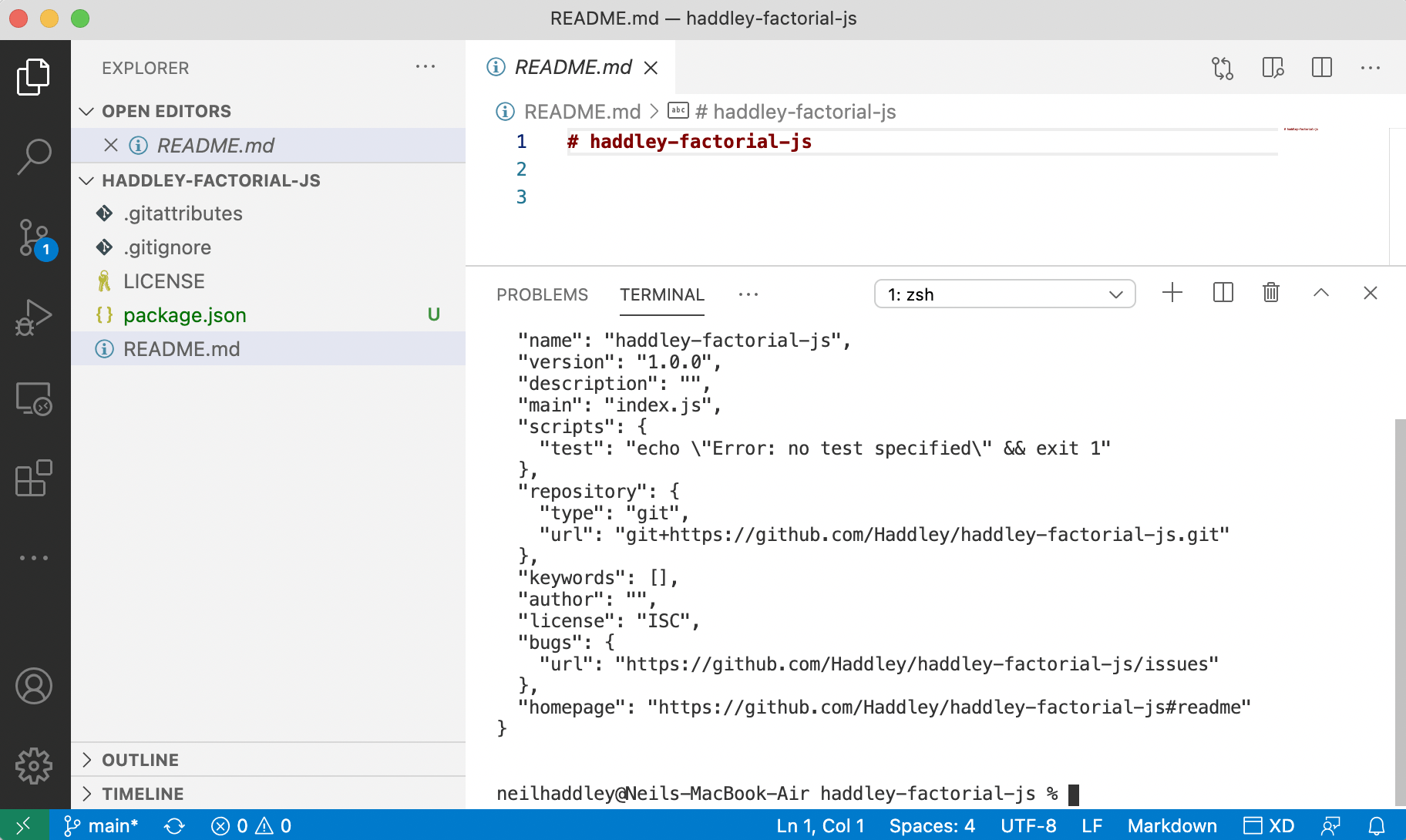
Image Description
index.js
Automated testing is added using mocha and chai.
$ npm i --save-dev mocha
$ npm i --save-dev chai
$ mkdir test
test/test.js
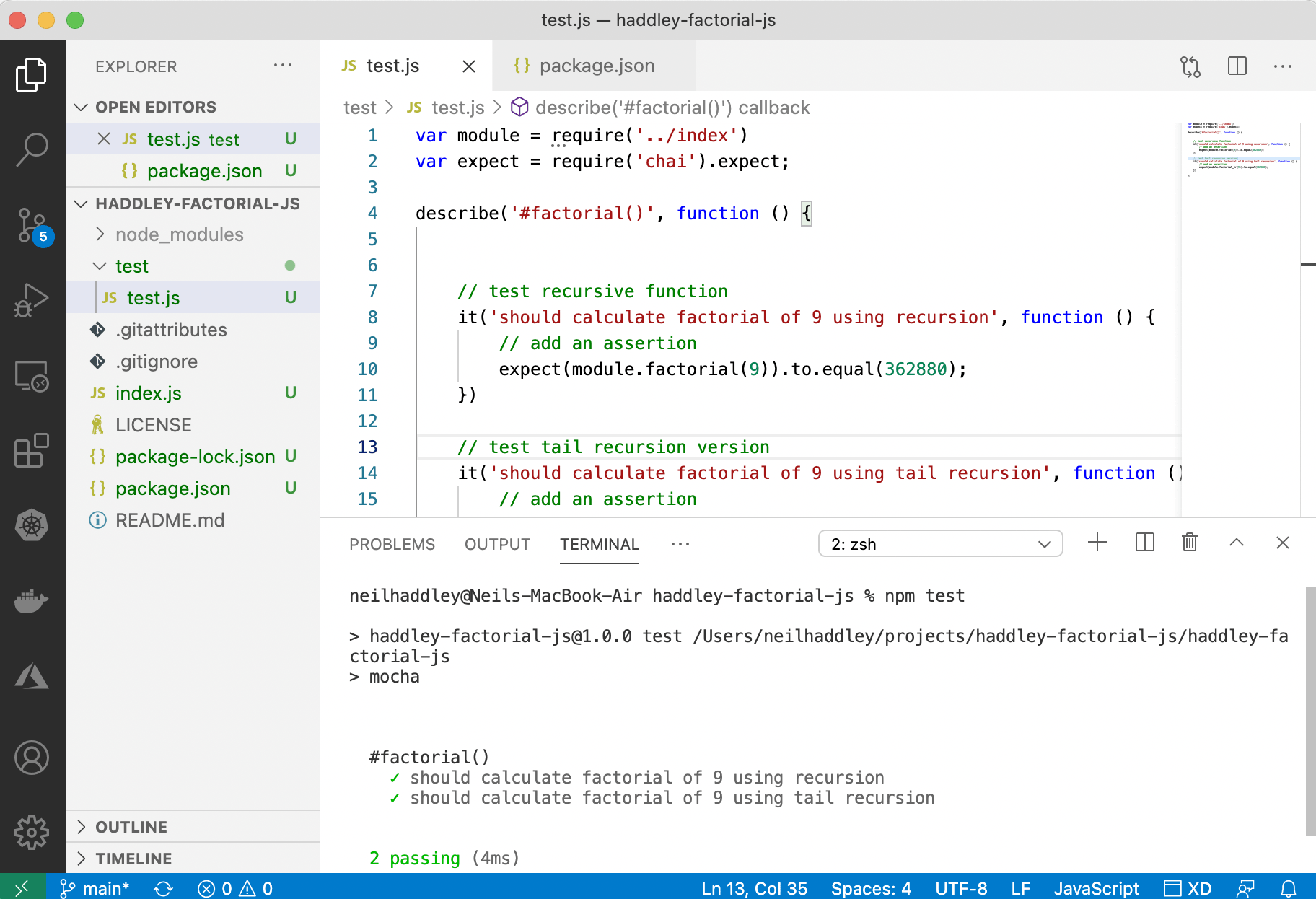
npm test
This is final package.json file
package.json
Github actions ensure that testing is performed using multiple versions of node.
node.js.yml
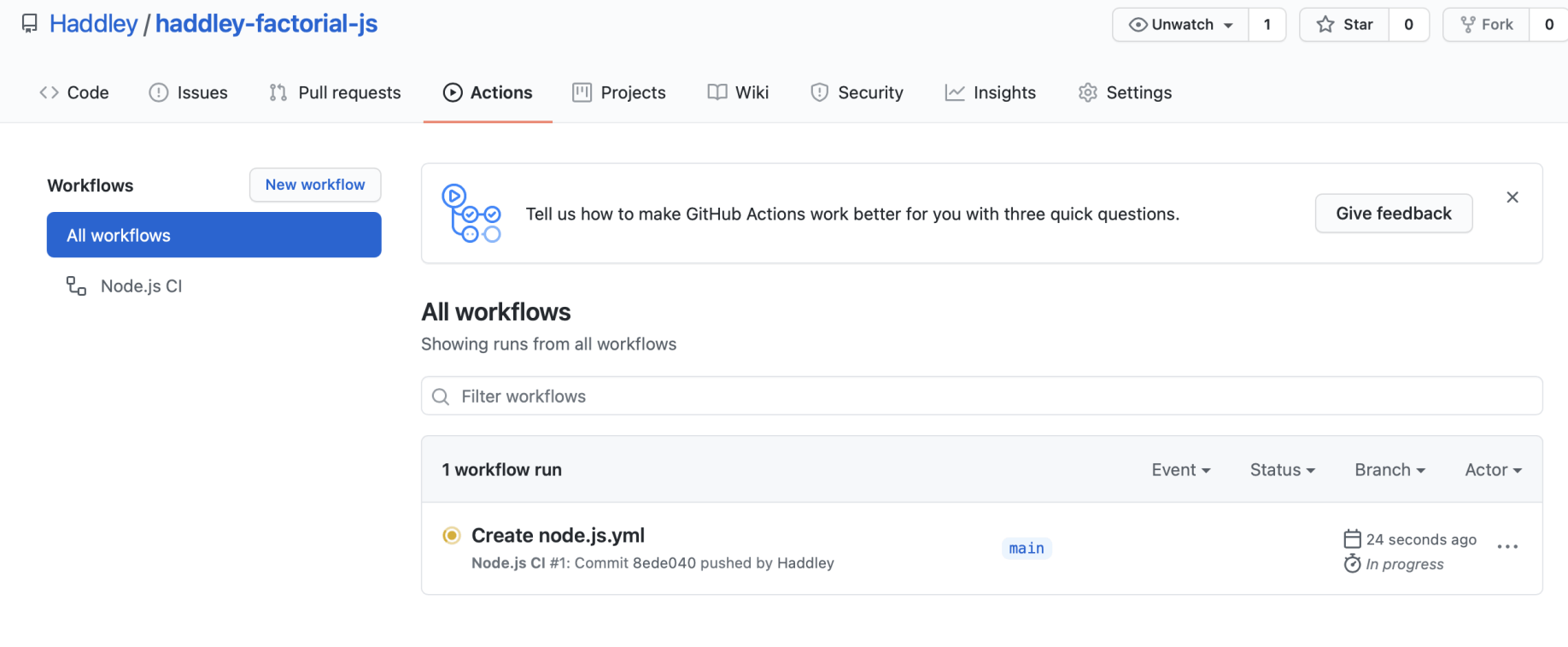
Tests are running
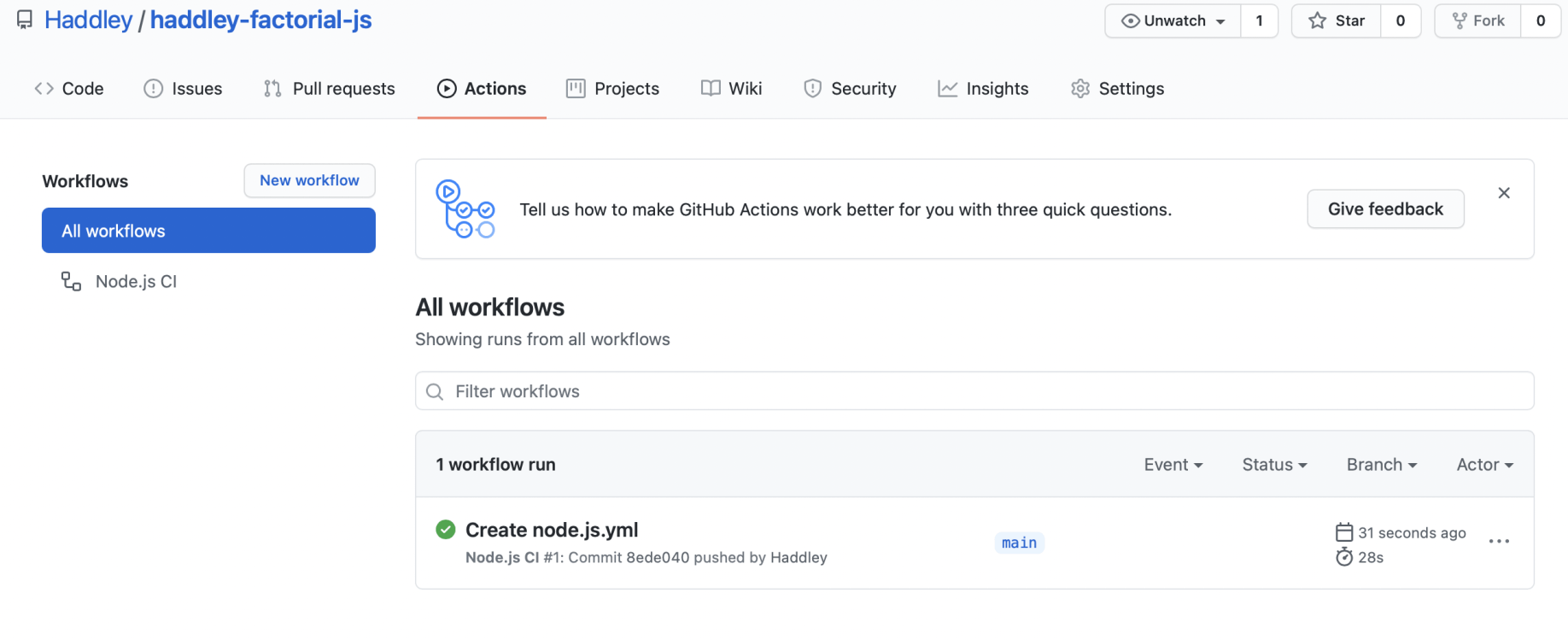
Code passed all of the provided tests
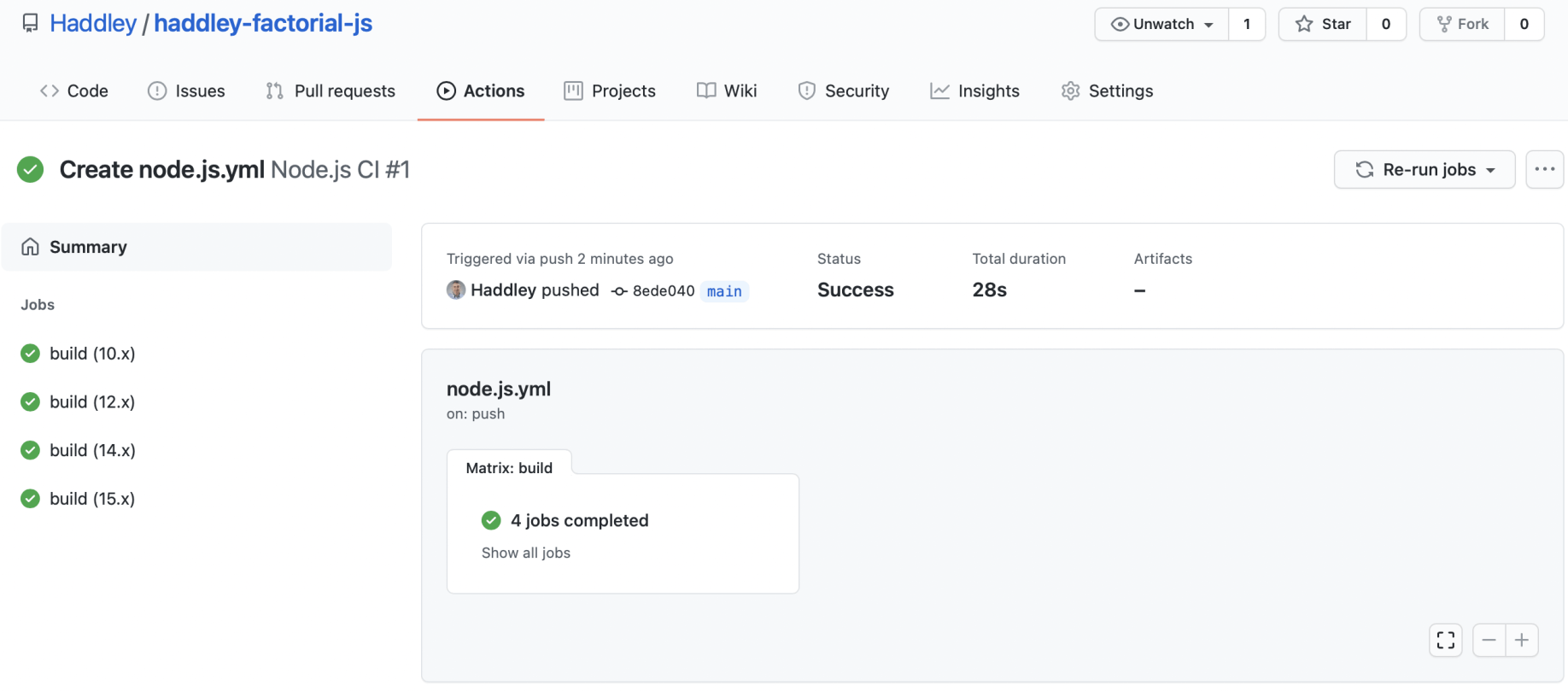
Test results for multiple versions of node
To publish the module to npmjs.com
$ node login
$ node publish
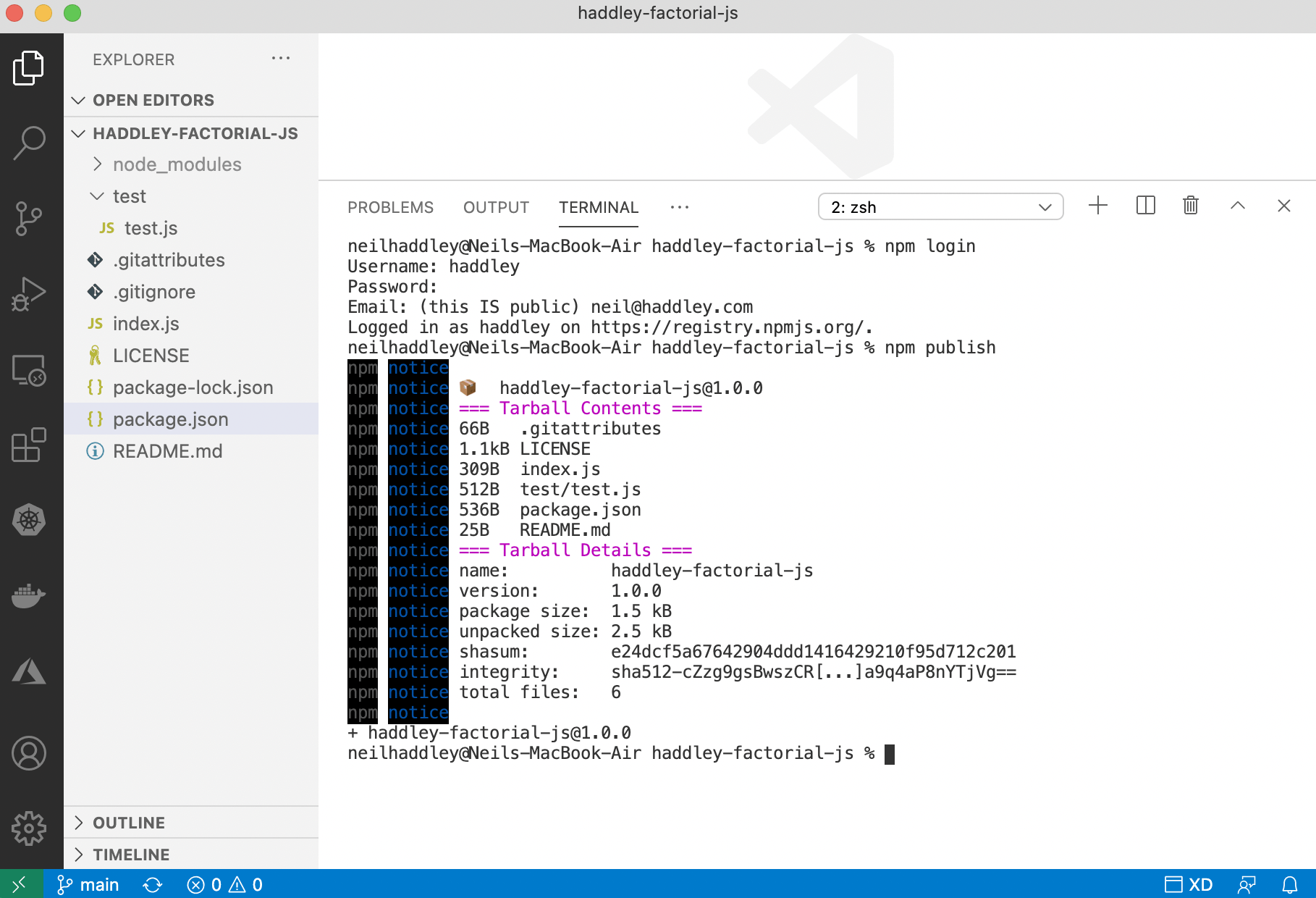
npm publish