Kubernetes
Neil Haddley • February 6, 2021
Kubernetes is a platform for managing containerized workloads.
Docker Desktop includes Kubernetes.
I deployed the haddley/blog container image using these commands:
BASH
1$ kubectl create deployment blog --image=haddley/blog --replicas=2 2 3$ kubectl expose deployment blog --type=LoadBalancer --port=8080 --target-port=80
Or I created a file called blog.yaml and used this command:
BASH
1$ kubectl apply -f .\blog.yaml
I adjusted the Kubernetes cluster by editing the yaml file below and "applying" the yaml file again.
I accessed one of the blog web servers by navigating to:
http://<ip address of the computer running Docker Desktop>:8080
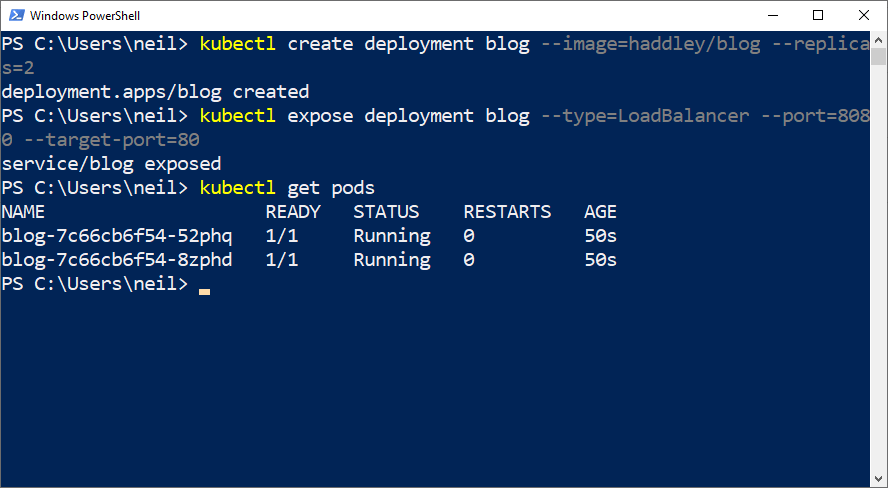
I used the "kubectl create deployment" and "kubectl expose deployment" commands
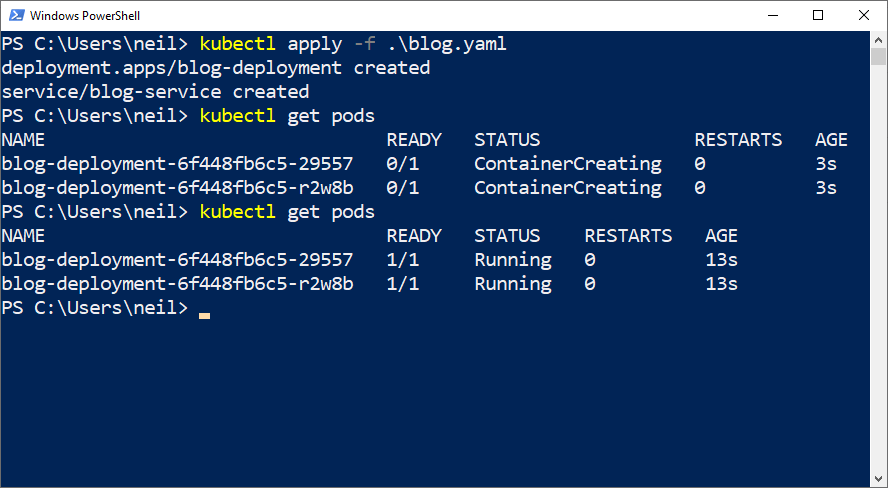
I used the "kubectl apply" command to apply a yaml file
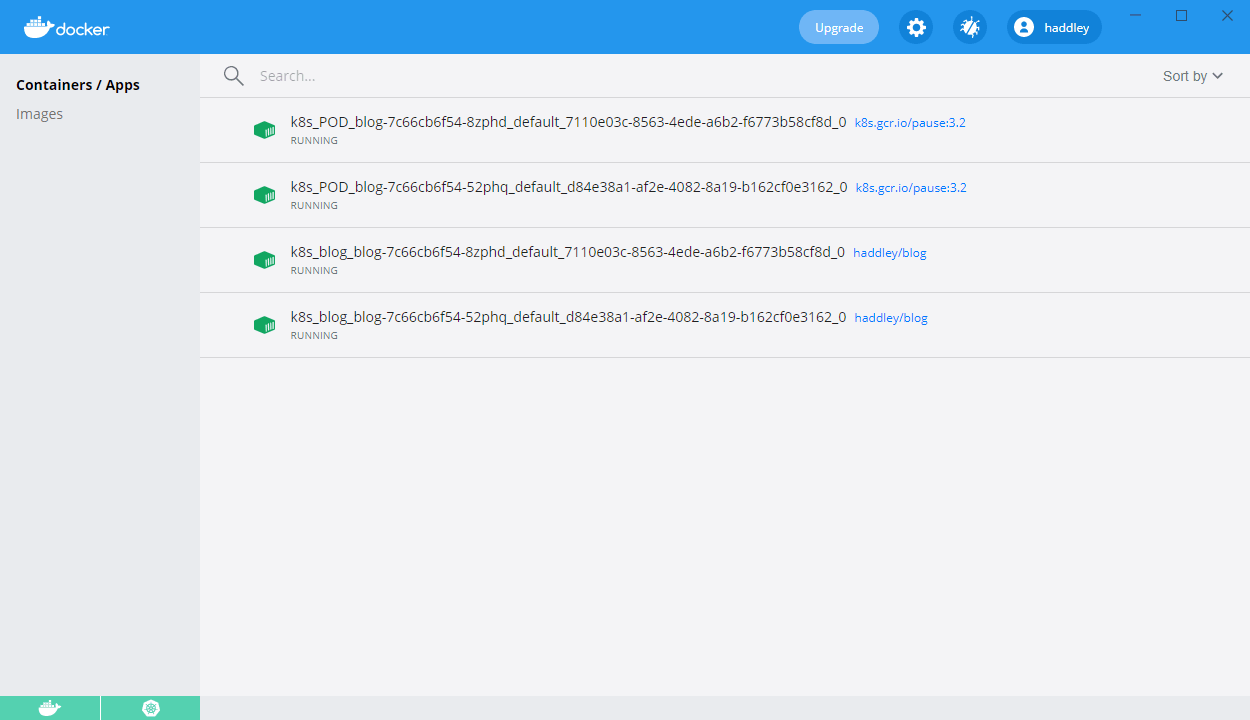
I ran the Docker image in two Kubernetes pods.
I accessed the cluster using port 8080
blog.yaml
YAML
1apiVersion: apps/v1 2kind: Deployment 3metadata: 4 name: blog-deployment 5 labels: 6 app: blog 7spec: 8 replicas: 2 9 selector: 10 matchLabels: 11 app: blog 12 template: 13 metadata: 14 labels: 15 app: blog 16 spec: 17 containers: 18 - name: blog 19 image: haddley/blog 20 resources: 21 limits: 22 memory: 512Mi 23 cpu: "1" 24 requests: 25 memory: 256Mi 26 cpu: "0.2" 27 ports: 28 - containerPort: 80 29--- 30apiVersion: v1 31kind: Service 32metadata: 33 name: blog-service 34spec: 35 selector: 36 app: blog 37 ports: 38 - protocol: TCP 39 port: 8080 40 targetPort: 80 41 type: LoadBalancer