Model Context Protocol (Part 1)
Neil Haddley • August 13, 2025
Typescript quick start
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a framework designed to enhance the reasoning and planning capabilities of AI agents.
In my Prompt flow with Semantic Kernel and Planner post I demonstrated that large language models rely on tools to do maths.
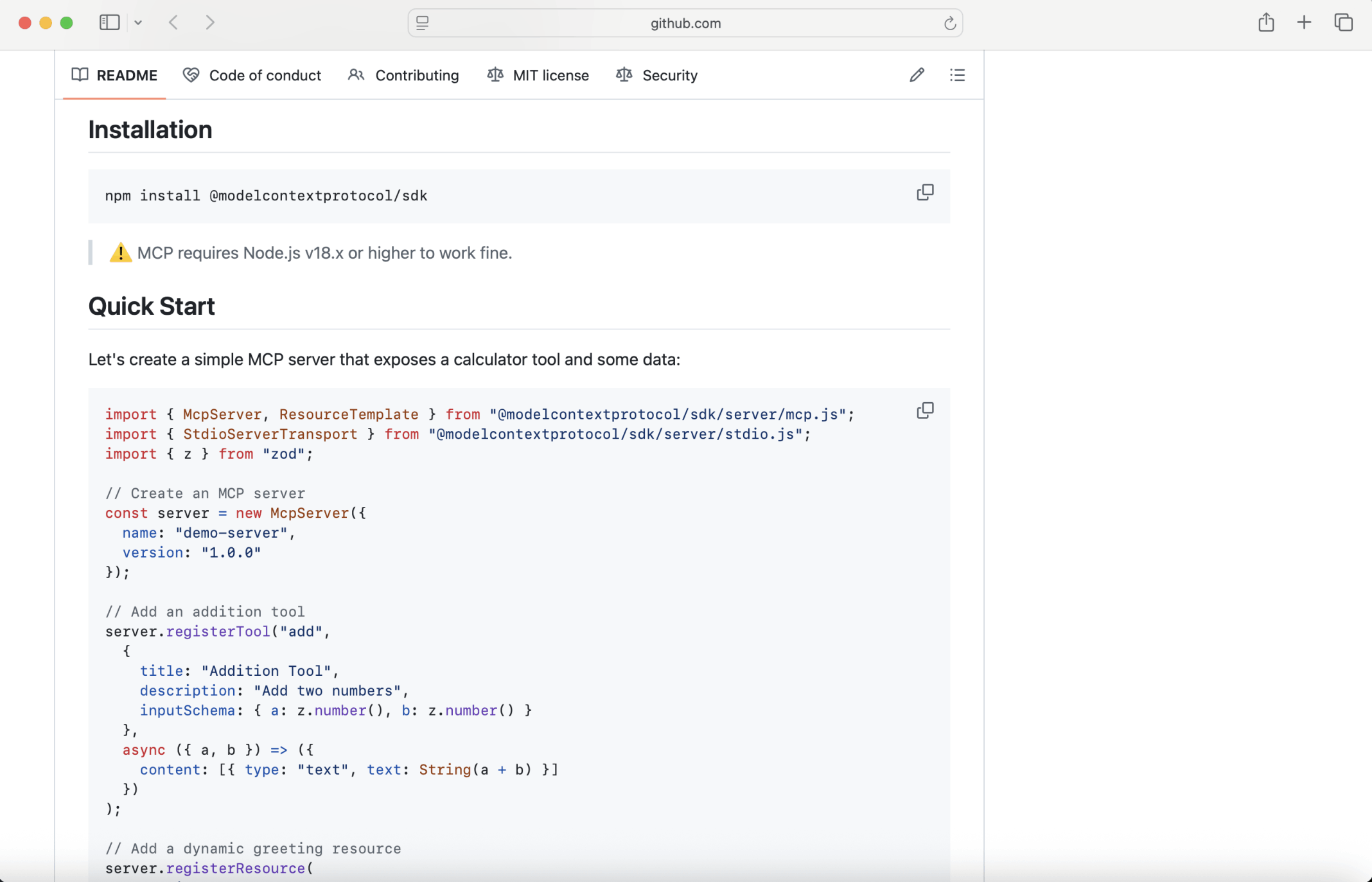
The model context protocol Typescript quick start demonstrates how to create a model context protocol server with an addition tool. I added a multiplication tool to the model context protocol sample (see the updated code below).
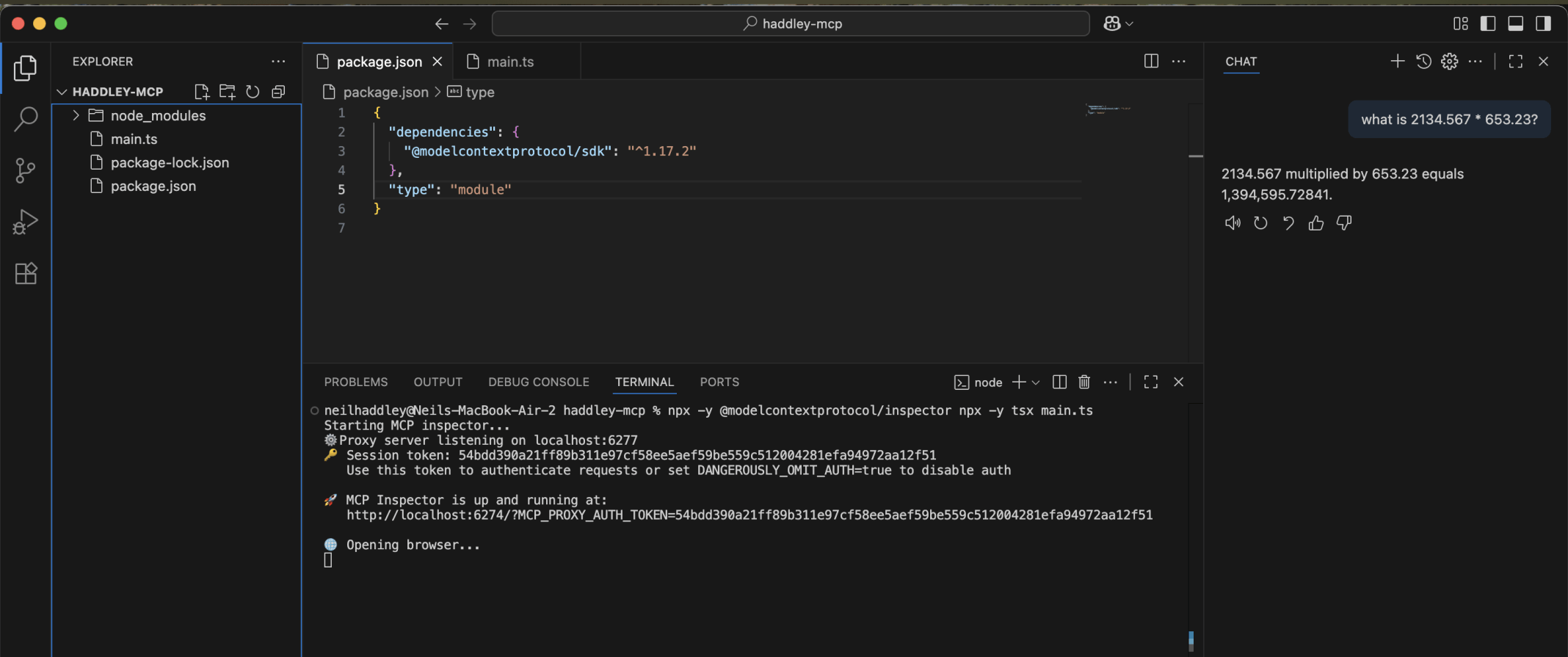
I used the model context protocol inspector to test the server
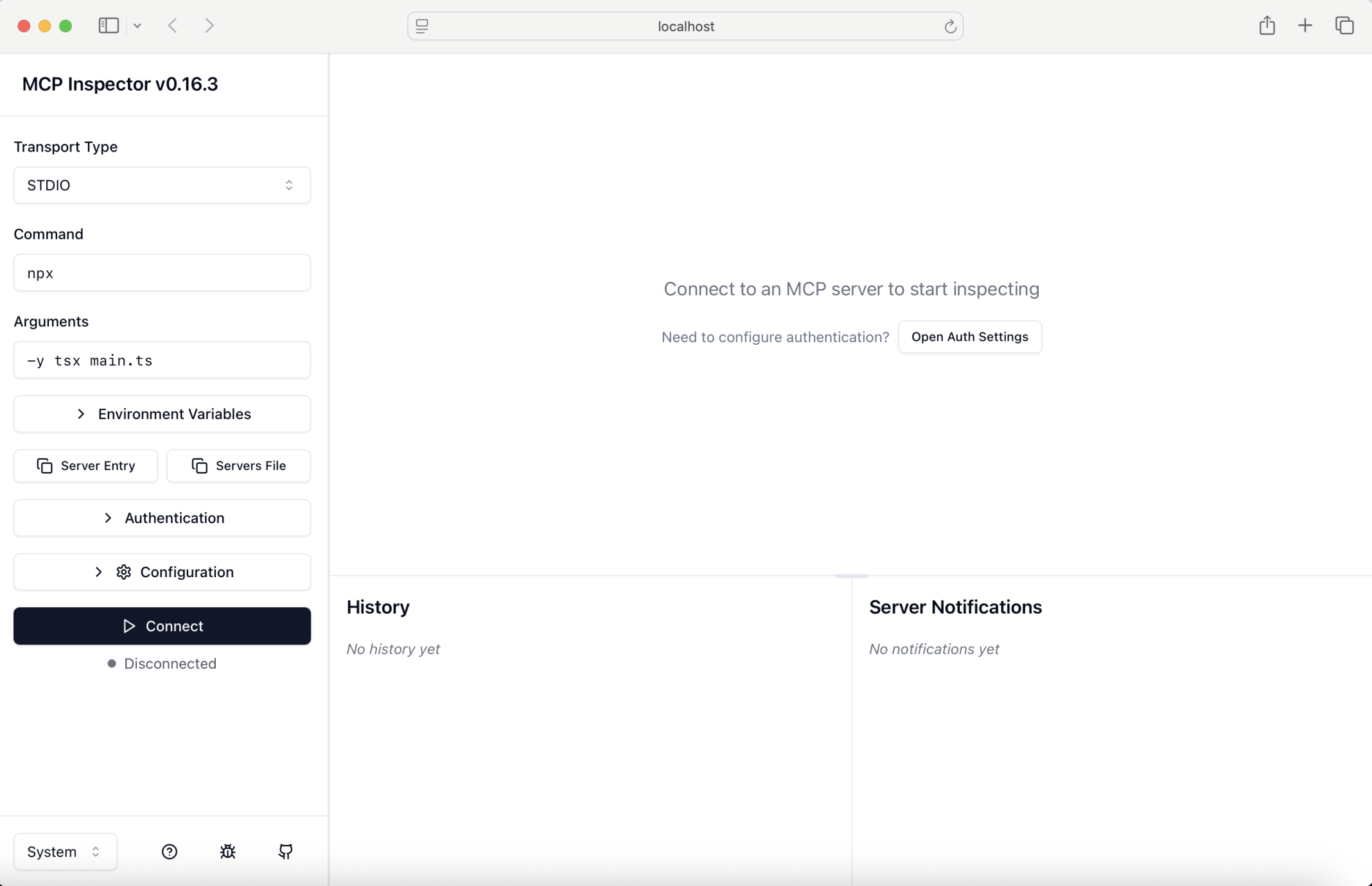
I clicked Connect
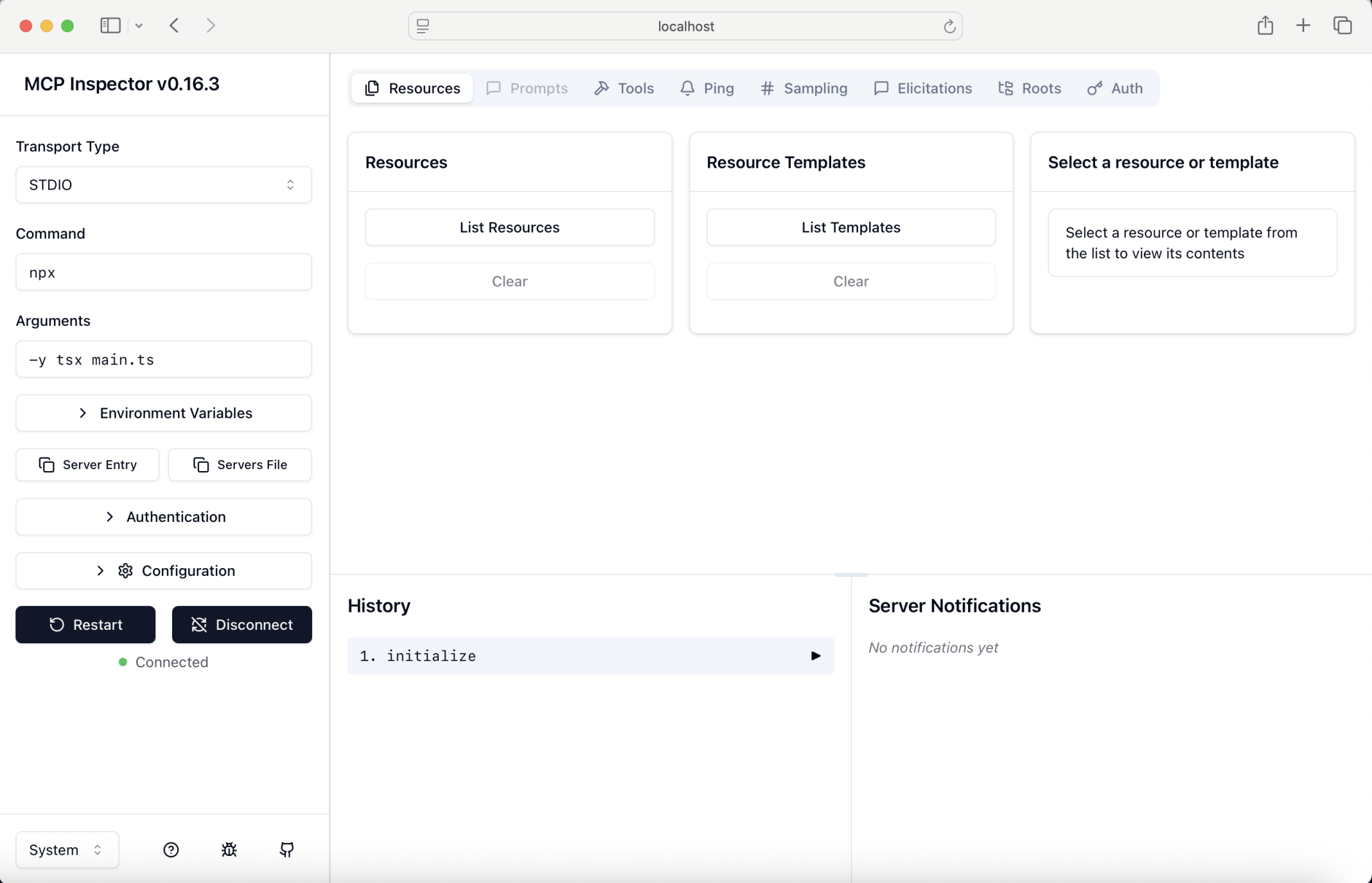
I clicked Tools
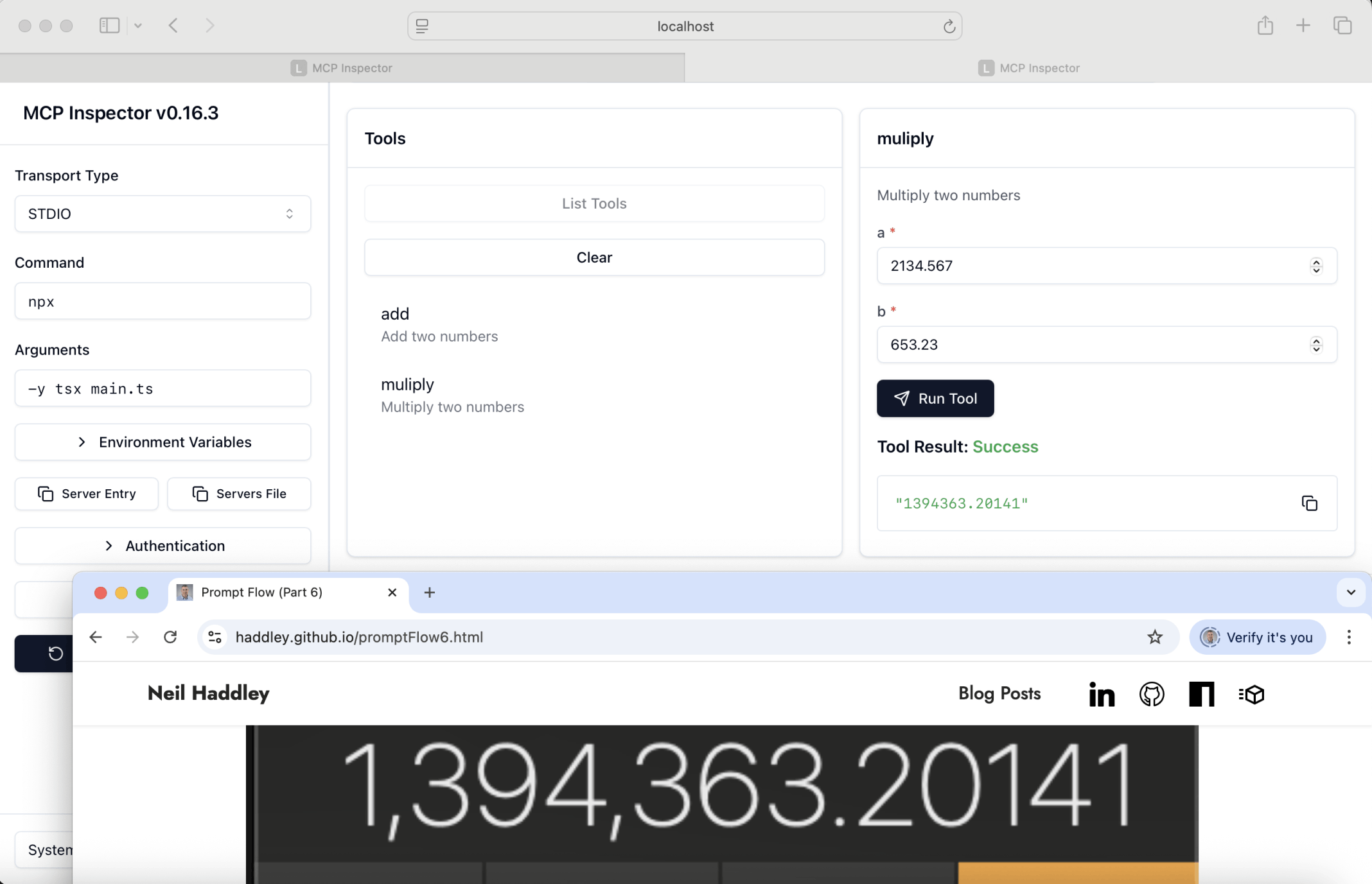
I clicked on the mulipy tool, entered arguments and clicked Run Tool
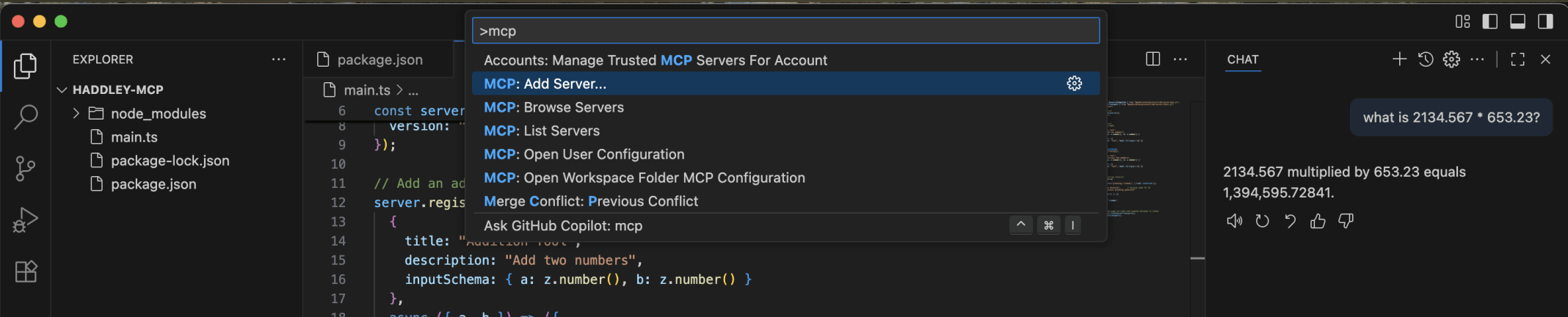
I clicked the Visual Studio Code Command Palette menu item and entered mcp
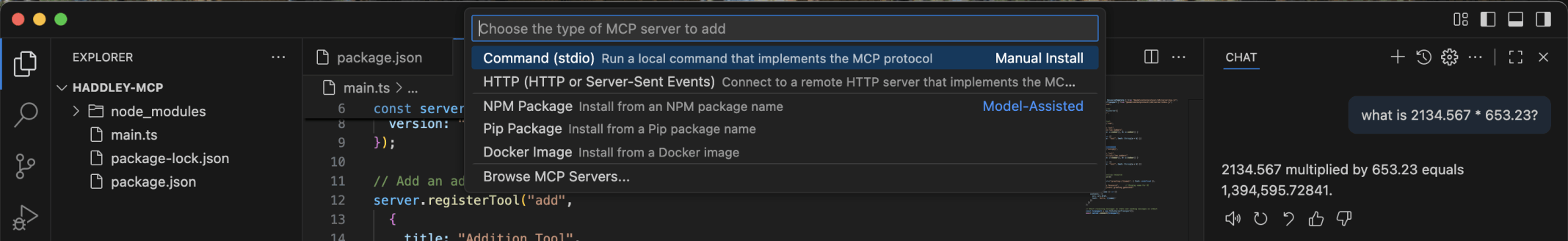
I selected Command
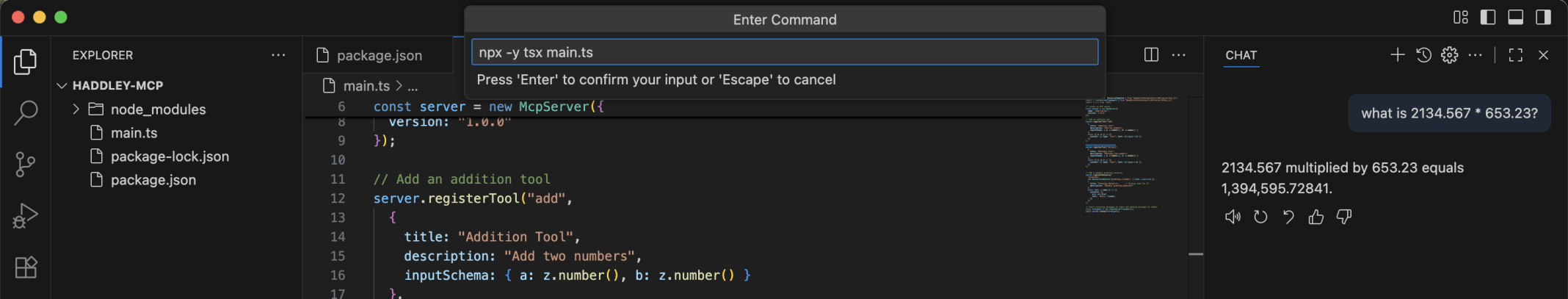
I entered the command needed to run the mcp server npx -y tsx main.ts
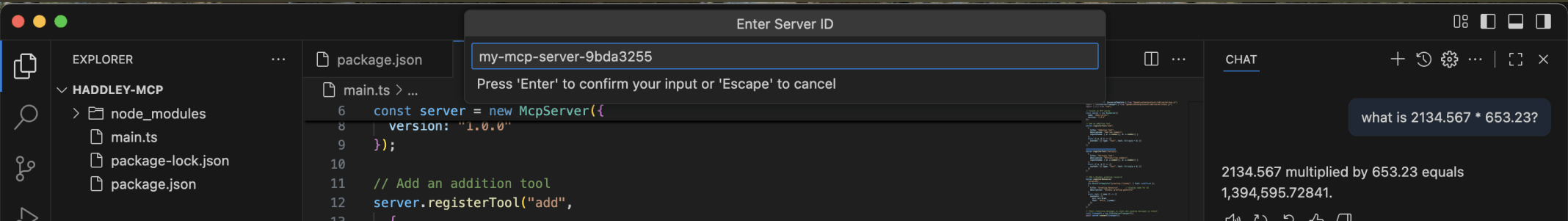
I accepted the generated name
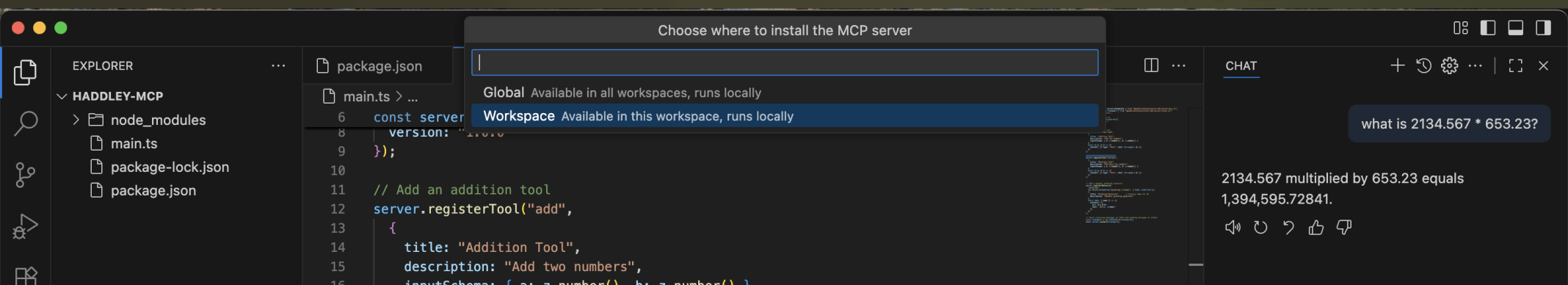
I selected Workspace
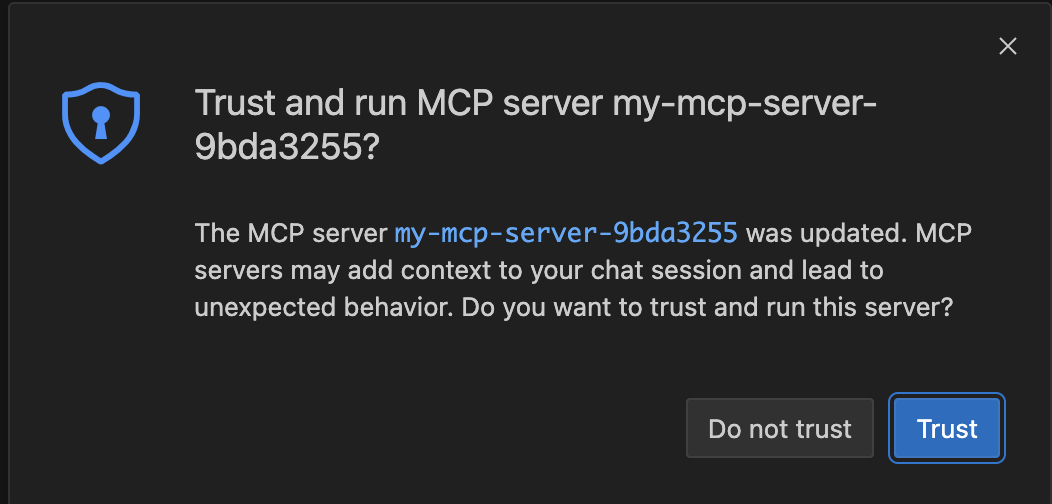
I clicked Trust
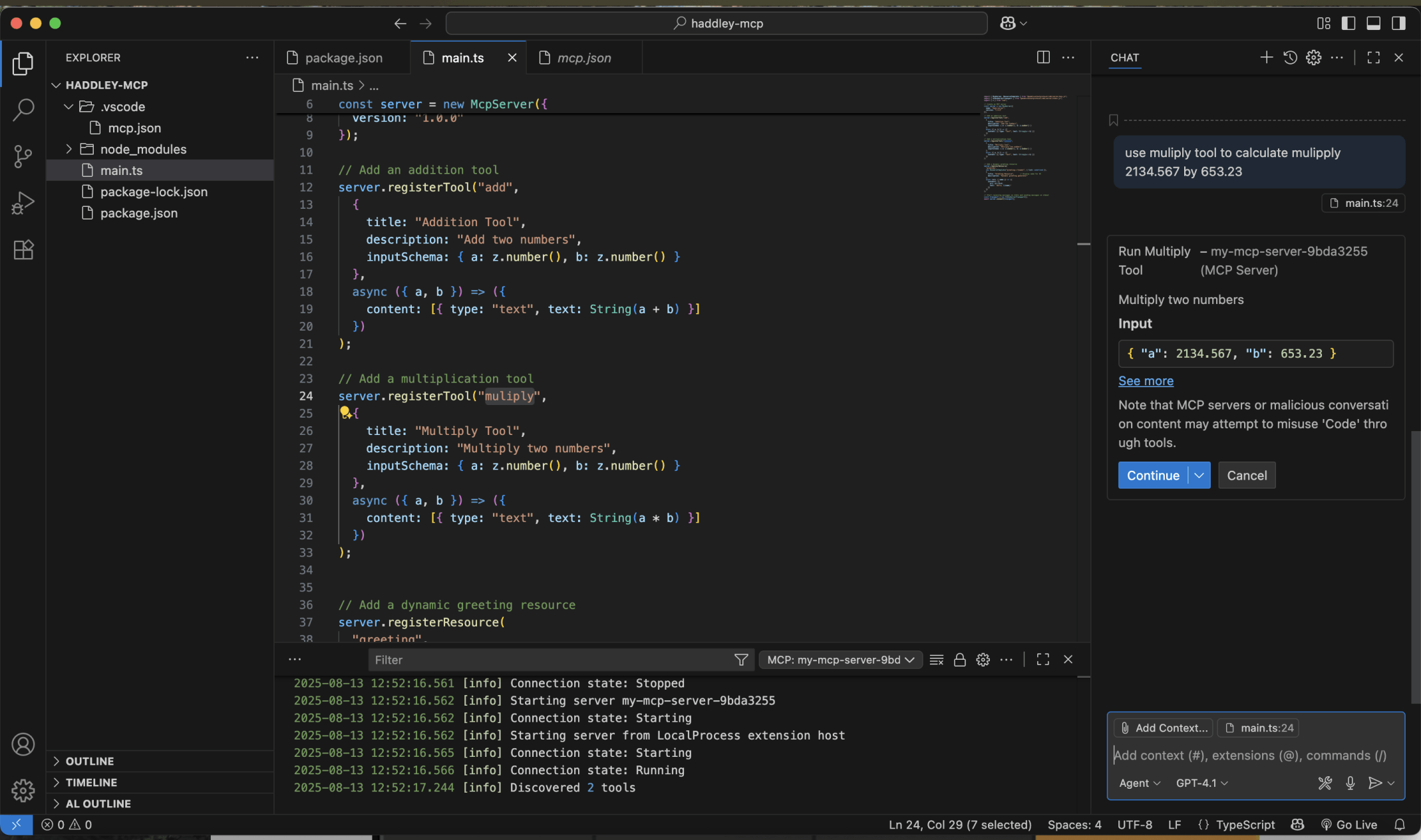
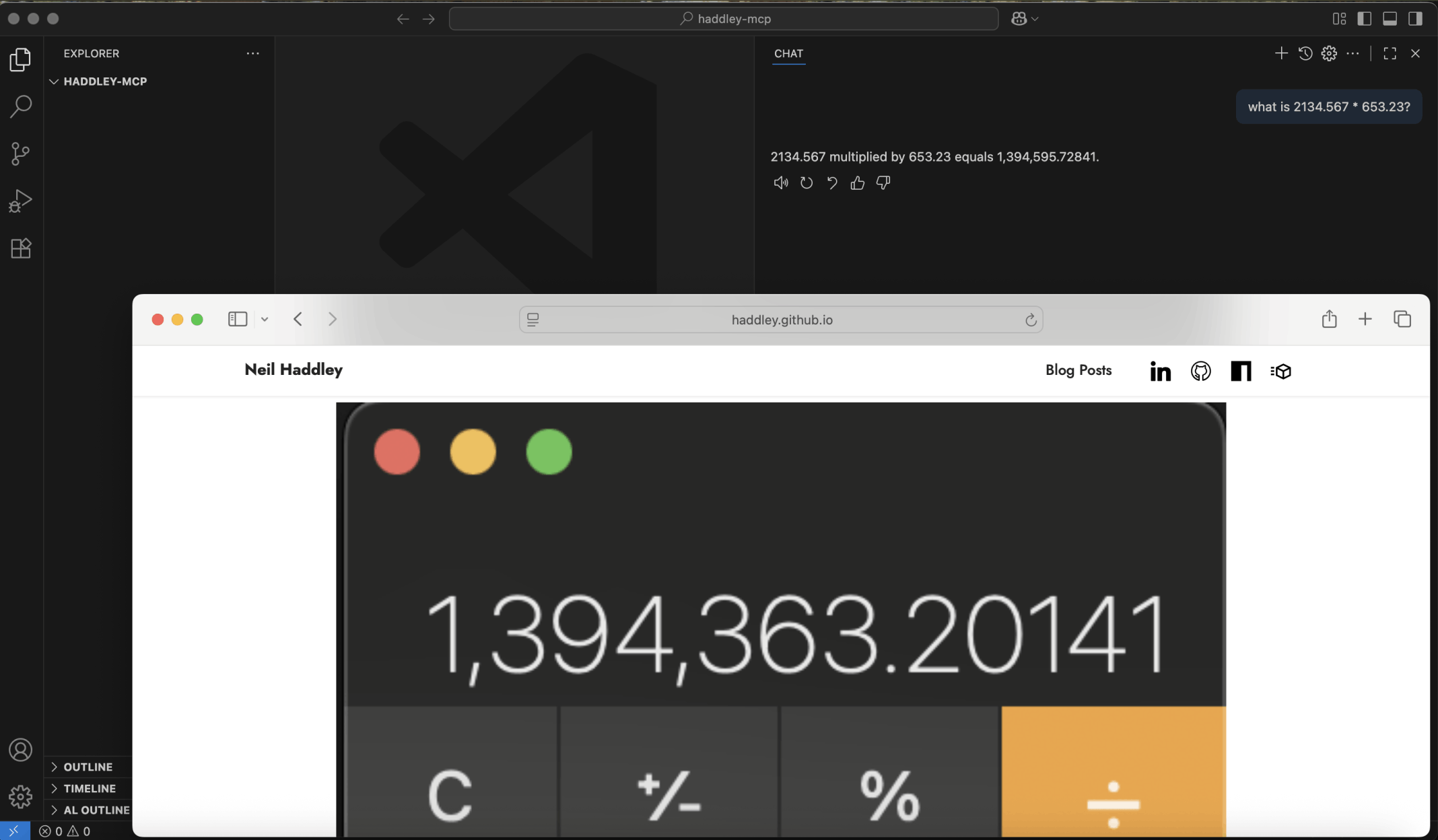
I used Visual Studio Code's chat window to ask the Large Language Model to multiply 2134.567 by 653.23
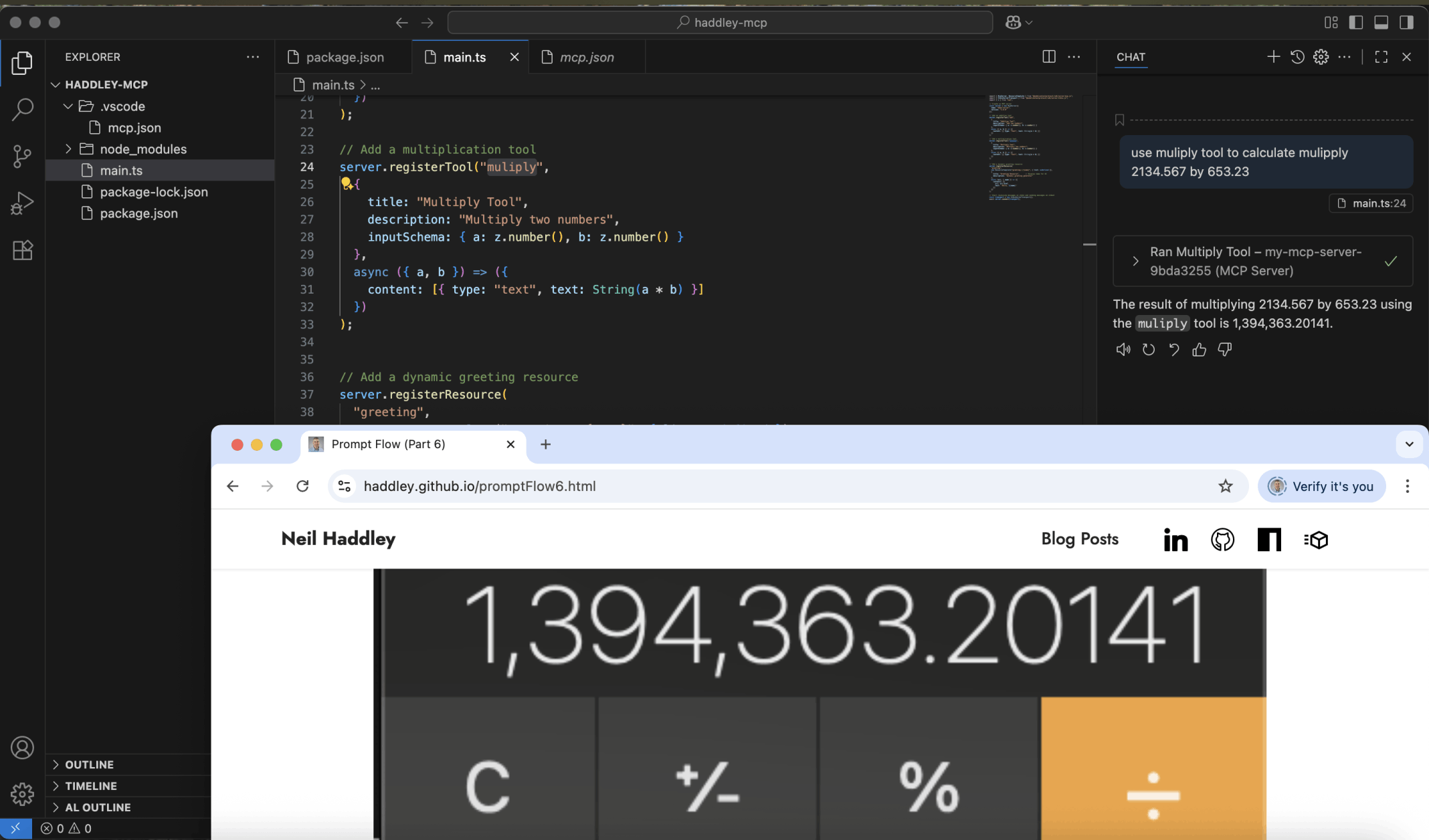
With the help of the multiply tool the Large Language Model was able to provide the correct answer
JAVASCRIPT
1import { McpServer, ResourceTemplate } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/mcp.js"; 2import { StdioServerTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/stdio.js"; 3import { z } from "zod"; 4 5// Create an MCP server 6const server = new McpServer({ 7 name: "demo-server", 8 version: "1.0.0" 9}); 10 11// Add an addition tool 12server.registerTool("add", 13 { 14 title: "Addition Tool", 15 description: "Add two numbers", 16 inputSchema: { a: z.number(), b: z.number() } 17 }, 18 async ({ a, b }) => ({ 19 content: [{ type: "text", text: String(a + b) }] 20 }) 21); 22 23// Add a multiplication tool 24server.registerTool("muliply", 25 { 26 title: "Multiply Tool", 27 description: "Multiply two numbers", 28 inputSchema: { a: z.number(), b: z.number() } 29 }, 30 async ({ a, b }) => ({ 31 content: [{ type: "text", text: String(a * b) }] 32 }) 33); 34 35 36// Add a dynamic greeting resource 37server.registerResource( 38 "greeting", 39 new ResourceTemplate("greeting://{name}", { list: undefined }), 40 { 41 title: "Greeting Resource", // Display name for UI 42 description: "Dynamic greeting generator" 43 }, 44 async (uri, { name }) => ({ 45 contents: [{ 46 uri: uri.href, 47 text: `Hello, ${name}!` 48 }] 49 }) 50); 51 52// Start receiving messages on stdin and sending messages on stdout 53const transport = new StdioServerTransport(); 54await server.connect(transport);