npm JavaScript
Neil Haddley • February 25, 2021
Create and publish an npm module using JavaScript.
Recursion
When a function is called, the computer must "remember" the place it was called from... so that it can return to that location with the result once the call is complete. Typically, this information is saved on the call stack... For tail calls, there is no need to remember the caller...
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tail_call
Some interpreters (and compilers) eliminate the stack frame creation and destruction work when they recognize tail recursion.
JavaScript
I created a folder for the new node module.
$ mkdir haddley-factorial-js
I navigated to the new folder.
$ cd haddley-factorial-js
I created a package.json file.
$ npm init -y
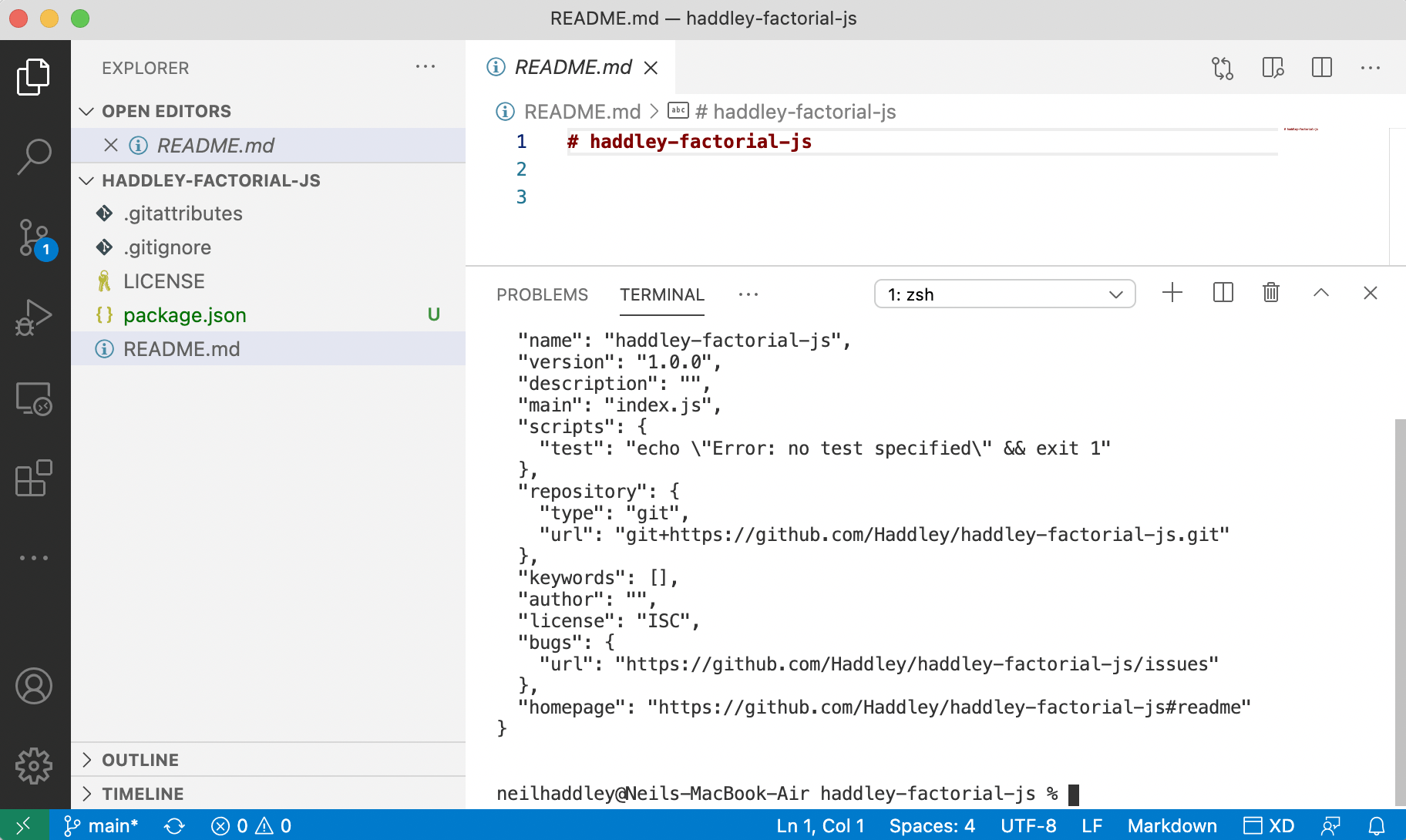
Image Description
Mocha and Chai
I added automated testing using mocha and chai.
$ npm i --save-dev mocha
$ npm i --save-dev chai
$ mkdir test
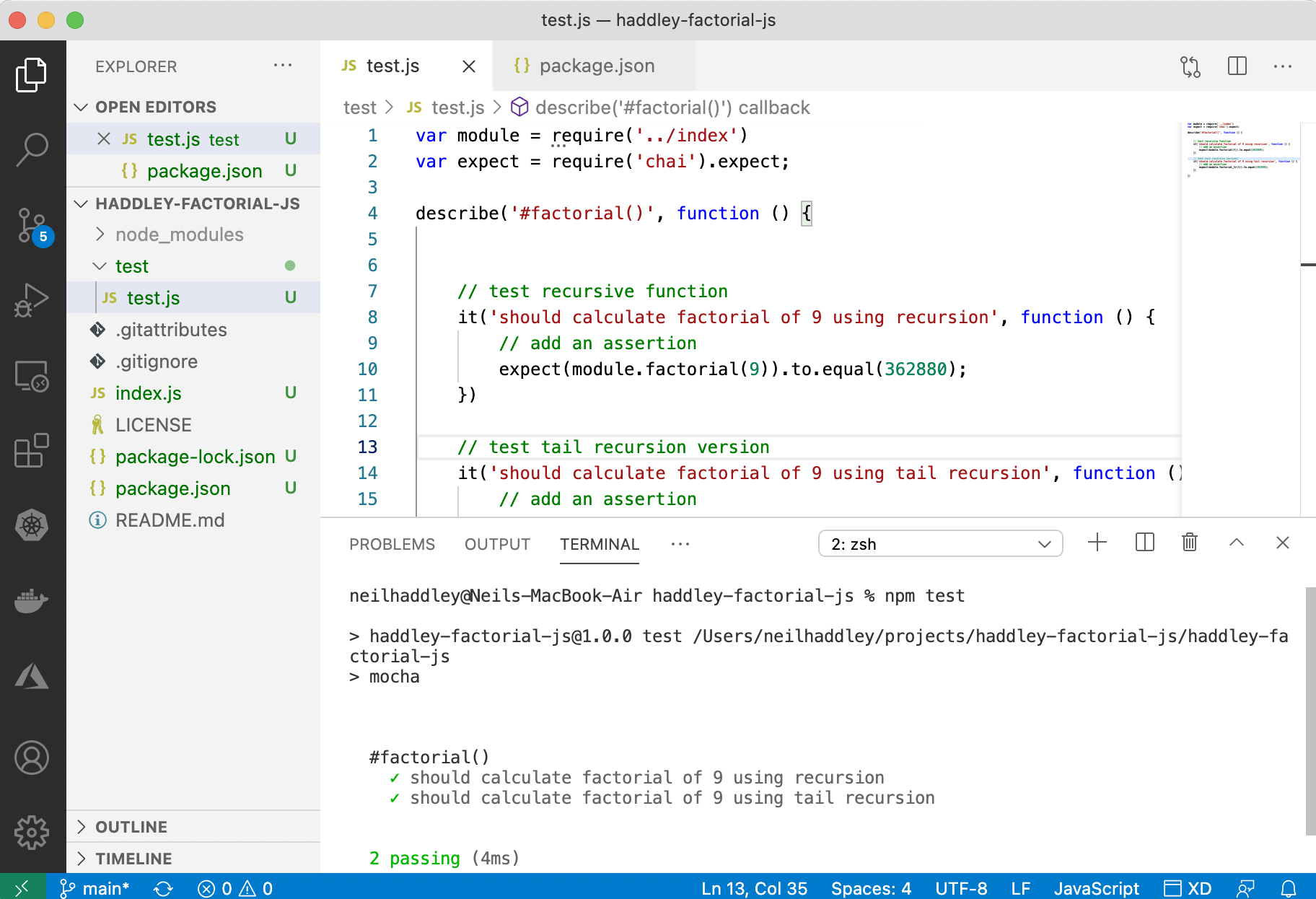
npm test
package.json
This is the final package.json file.
Github actions
I used GitHub Actions to run tests across multiple versions of Node.
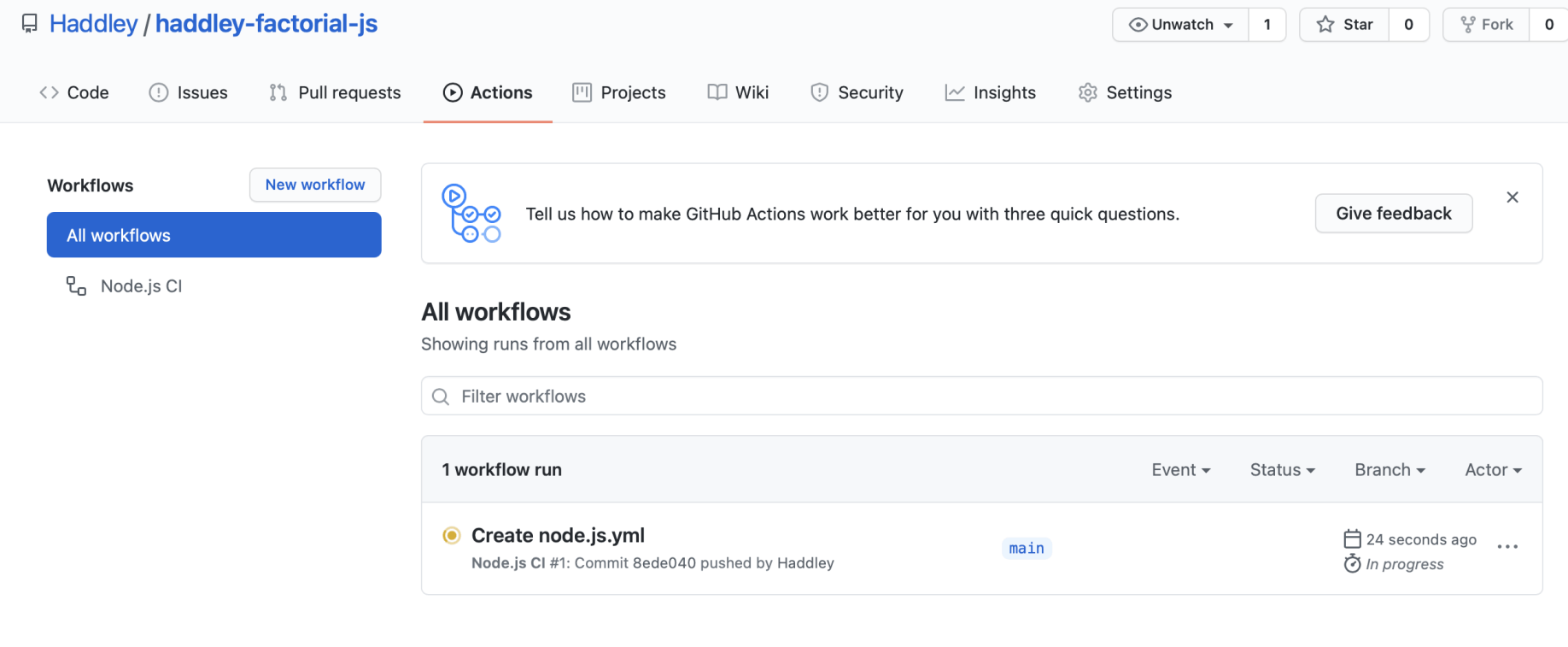
The tests ran
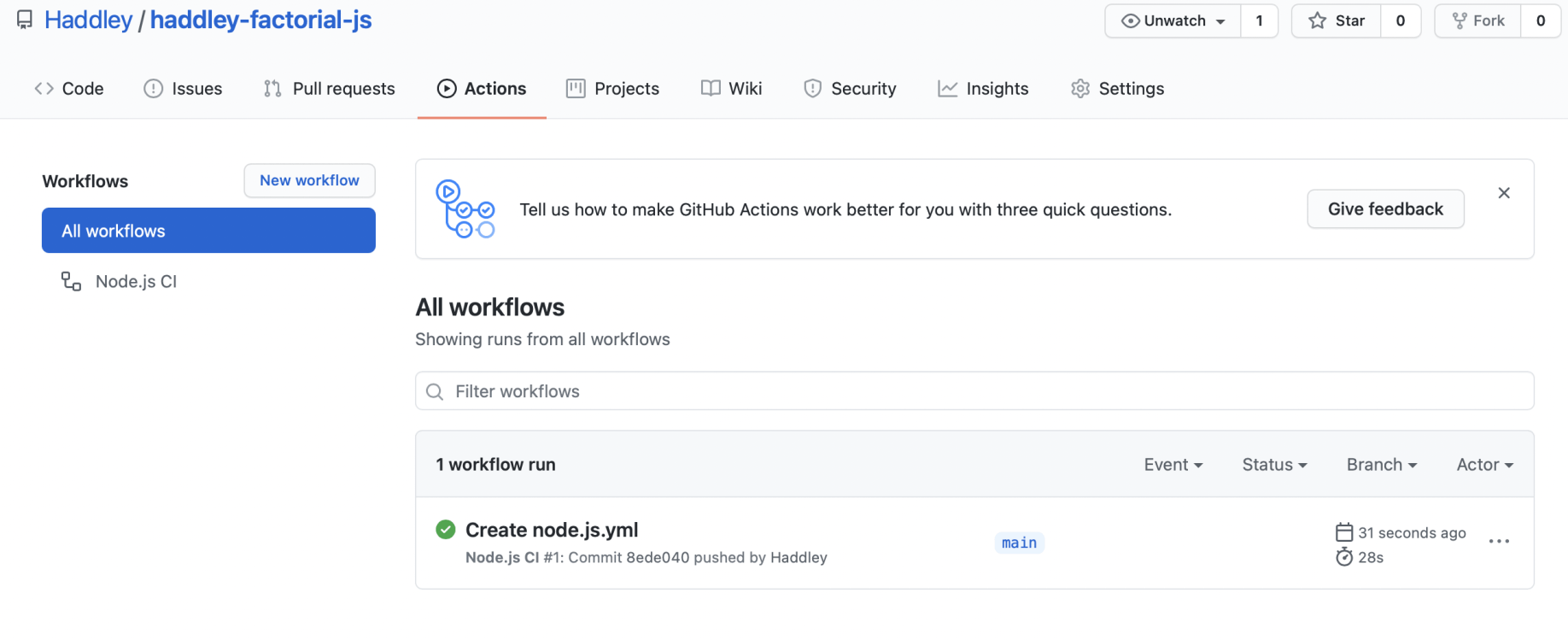
The code passed all tests
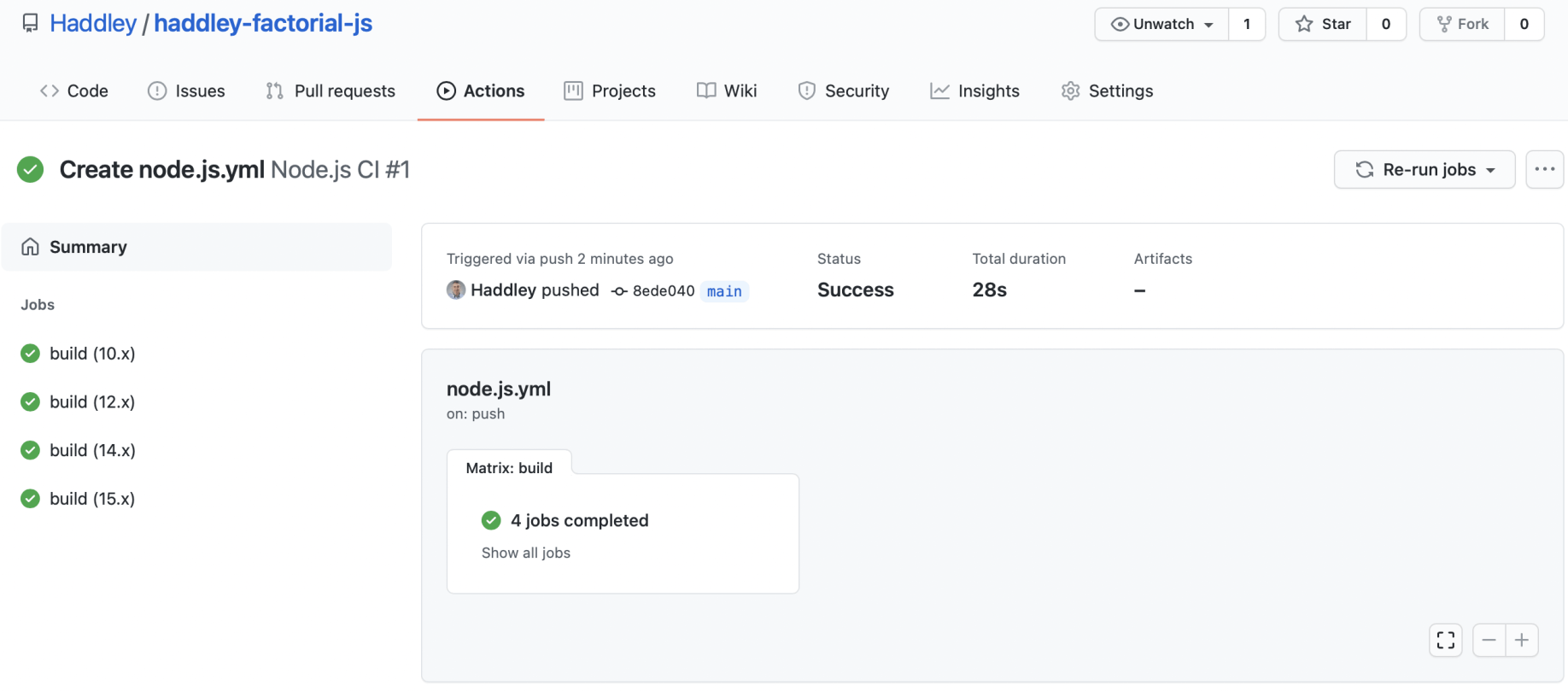
Test results for multiple versions of node
Publishing to npmjs.com
I published the module to npmjs.com.
$ node login
$ node publish
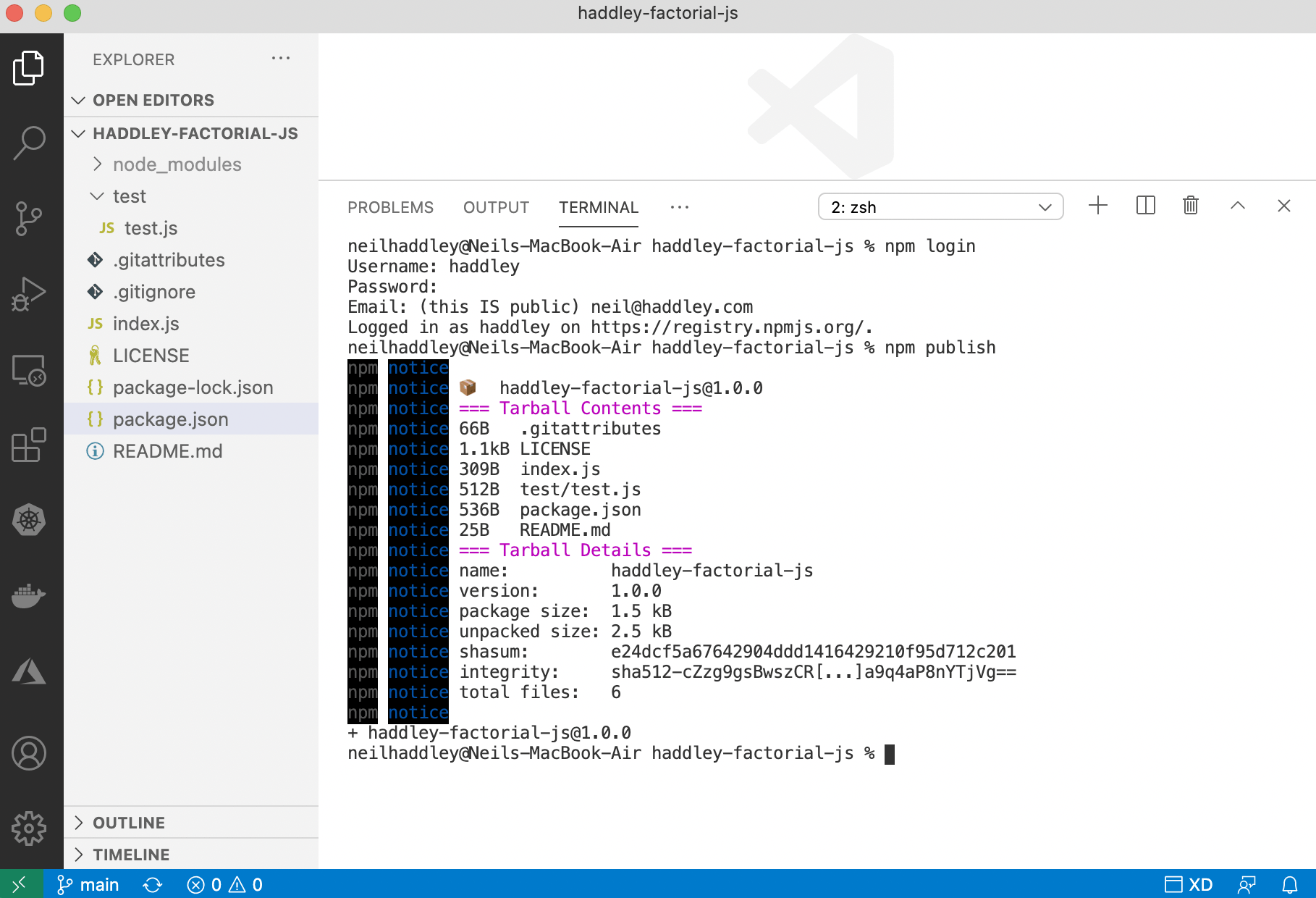
npm publish
index.js
JAVASCRIPT
1const factorial = (n) => { 2 if (n < 2) return 1; 3 return n * factorial(n - 1); 4} 5 6exports.factorial = factorial 7 8const factorial_tr = (n) => { 9 10 function fact(n, acc) { 11 if (n < 2) return acc; 12 return fact(n - 1, n * acc); 13 } 14 15 return fact(n, 1) 16} 17 18exports.factorial_tr = factorial_tr 19 20const factorial_it = (n) => { 21 22 let acc = 1 23 24 for (i = n; i > 1; i--) { 25 acc = acc * i 26 } 27 28 return acc 29} 30 31exports.factorial_it = factorial_it
testtest.js
JAVASCRIPT
1var module = require('../index') 2var expect = require('chai').expect; 3 4describe('#factorial()', function () { 5 6 // test recursive function 7 it('should calculate factorial of 9 using recursion', function () { 8 // add an assertion 9 expect(module.factorial(9)).to.equal(362880); 10 }) 11 12 // test tail recursion version 13 it('should calculate factorial of 9 using tail recursion', function () { 14 // add an assertion 15 expect(module.factorial_tr(9)).to.equal(362880); 16 }) 17 18 // test iteration version 19 it('should calculate factorial of 9 using iteration', function () { 20 // add an assertion 21 expect(module.factorial_it(9)).to.equal(362880); 22 }) 23 24 // test tail recursion version 25 it('should calculate factorial of 170 using recursion', function () { 26 // add an assertion 27 expect(module.factorial(170)).to.equal(7.257415615307994e+306); 28 }) 29 30 // test tail recursion version 31 it('should calculate factorial of 170 using tail recursion', function () { 32 // add an assertion 33 expect(module.factorial_tr(170)).to.equal(7.257415615308004e+306); 34 }) 35 36 // test iteration version 37 it('should calculate factorial of 170 using iteration', function () { 38 // add an assertion 39 expect(module.factorial_it(170)).to.equal(7.257415615308004e+306); 40 }) 41 42 // test tail recursion version 43 it('should calculate factorial of 171 using recursion', function () { 44 // add an assertion 45 expect(module.factorial(171)).to.equal(Infinity); 46 }) 47 48 // test tail recursion version 49 it('should calculate factorial of 171 using tail recursion', function () { 50 // add an assertion 51 expect(module.factorial_tr(171)).to.equal(Infinity); 52 }) 53 54 // test iteration version 55 it('should calculate factorial of 171 using iteration', function () { 56 // add an assertion 57 expect(module.factorial_it(171)).to.equal(Infinity); 58 }) 59 60 // test recursive function 61 it('should calculate factorial of 10000 using recursion', function () { 62 this.timeout(10000); 63 // add an assertion 64 expect(module.factorial(10000)).to.equal(Infinity); 65 }) 66 67 // test recursive function 68 it('should calculate factorial of 10000 using tail recursion', function () { 69 this.timeout(10000); 70 // add an assertion 71 expect(module.factorial_tr(10000)).to.equal(Infinity); 72 }) 73 74 // test recursive function 75 it('should calculate factorial of 1600000 using iteration', function () { 76 this.timeout(10000); 77 // add an assertion 78 expect(module.factorial_it(1600000)).to.equal(Infinity); 79 }) 80 81 82})
package.json
JAVASCRIPT
1{ 2 "name": "haddley-factorial-js", 3 "version": "1.0.0", 4 "description": "", 5 "main": "index.js", 6 "scripts": { 7 "test": "mocha" 8 }, 9 "repository": { 10 "type": "git", 11 "url": "git+https://github.com/Haddley/haddley-factorial-js.git" 12 }, 13 "keywords": [], 14 "author": "", 15 "license": "ISC", 16 "bugs": { 17 "url": "https://github.com/Haddley/haddley-factorial-js/issues" 18 }, 19 "homepage": "https://github.com/Haddley/haddley-factorial-js#readme", 20 "devDependencies": { 21 "chai": "^4.3.0", 22 "mocha": "^8.3.0" 23 } 24}
node.js.yml
JAVASCRIPT
1# This workflow will do a clean install of node dependencies, build the source code and run tests across different versions of node 2# For more information see: https://help.github.com/actions/language-and-framework-guides/using-nodejs-with-github-actions 3 4name: Node.js CI 5 6on: 7 push: 8 branches: [ main ] 9 pull_request: 10 branches: [ main ] 11 12jobs: 13 build: 14 15 runs-on: ubuntu-latest 16 17 strategy: 18 matrix: 19 node-version: [10.x, 12.x, 14.x, 15.x] 20 # See supported Node.js release schedule at https://nodejs.org/en/about/releases/ 21 22 steps: 23 - uses: actions/checkout@v2 24 - name: Use Node.js ${{ matrix.node-version }} 25 uses: actions/setup-node@v1 26 with: 27 node-version: ${{ matrix.node-version }} 28 - run: npm ci 29 - run: npm run build --if-present 30 - run: npm test