This is the logo owned by Apple Inc. for Xcode. Taken from the picture's app bundle. Fair use
This is the logo owned by Apple Inc. for Xcode. Taken from the picture's app bundle. Fair use
OpenGL Mathematics (GLM) is a header only C++ mathematics library for graphics software based on the OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) specifications.
I installed GLM using this command
$ brew install glm
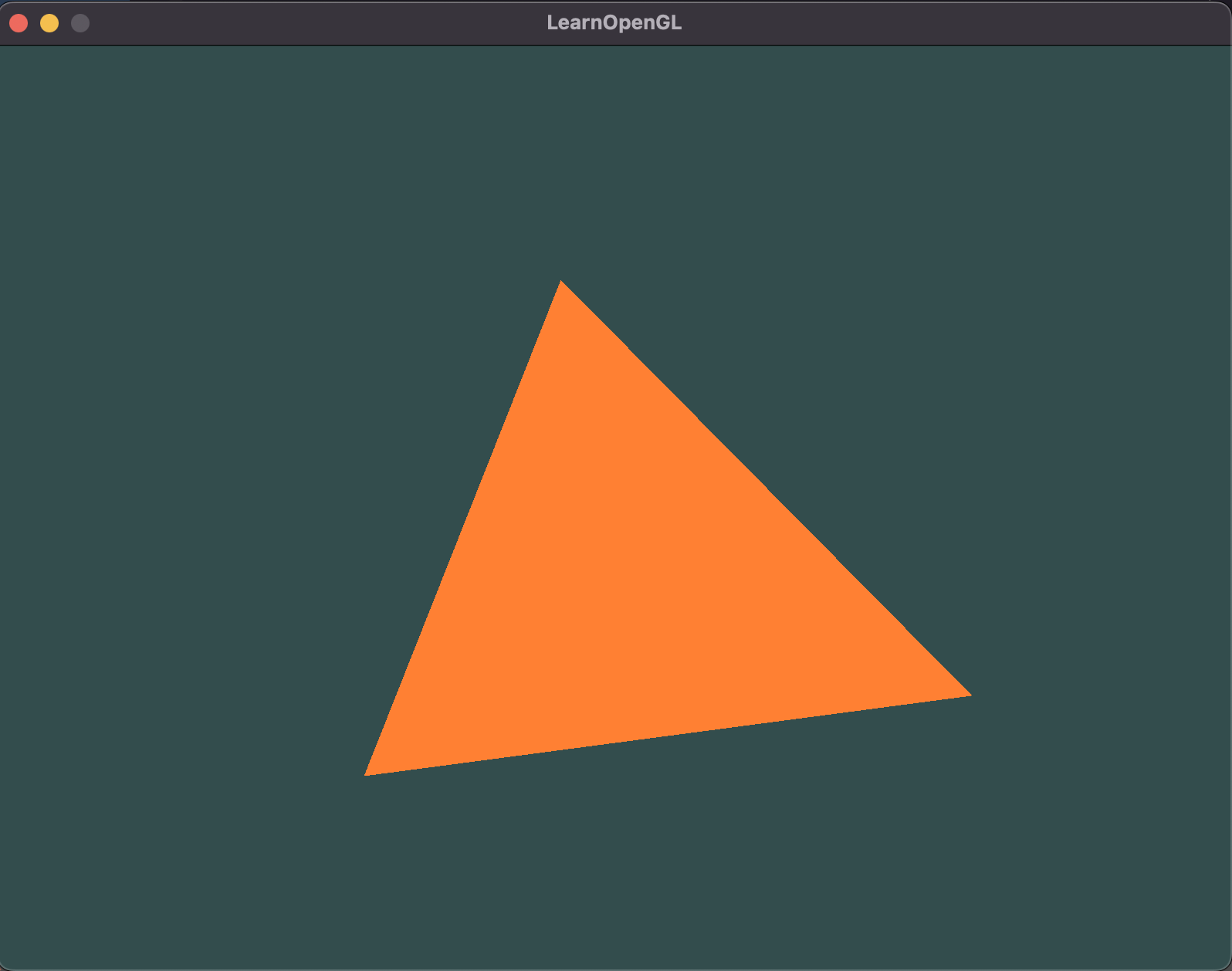
Running application
To rotate the triangle by 10 degrees I had to make changes to the vertex shader.
I had to update the code to apply a rotation matrix to the vertex positions.
const GLchar* vertexShaderSource = "#version 330 core\n"
"layout (location = 0) in vec3 position;\n"
"uniform mat4 transform;\n"
"void main()\n"
"{\n"
"gl_Position = transform * vec4(position, 1.0);\n"
"}\0";
In the updated code the uniform variable "transform" represents the rotation matrix that will be applied to the vertex positions.
To set the value of the transform uniform, I needed to add some code to the main function.
To rotate the triangle by 10 degrees around the z-axis I added this code
// Define the rotation angle in degrees
GLfloat angle = 10.0f;
// Convert the angle to radians
GLfloat radians = glm::radians(angle);
// Calculate the rotation matrix
glm::mat4 rotation = glm::rotate(glm::mat4(1.0f), radians, glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f));
// Get the location of the "transform" uniform
GLint transformLoc = glGetUniformLocation(shaderProgram, "transform");
// Set the value of the "transform" uniform
glUniformMatrix4fv(transformLoc, 1, GL_FALSE, glm::value_ptr(rotation));
A rotation matrix "rotation" is calculated using the glm::rotate() function.
The glm::rotate() function takes a matrix, an angle (in radians), and an axis of rotation (In this case, we are rotating around the z-axis, so we pass in a vector with x and y values of 0 and a z value of 1).
The location of the transform uniform in the vertex shader is retrieved using the glGetUniformLocation() function.
The value of the transform uniform is set using the glUniformMatrix4fv() function, which takes the location of the uniform, the number of matrices being passed (1), whether or not to transpose the matrix (in this case, we don't want to transpose it), and a pointer to the matrix data (which is obtained using the glm::value_ptr() function).
With these changes, the triangle is rotated by 10 degrees around the z-axis.
main.cpp
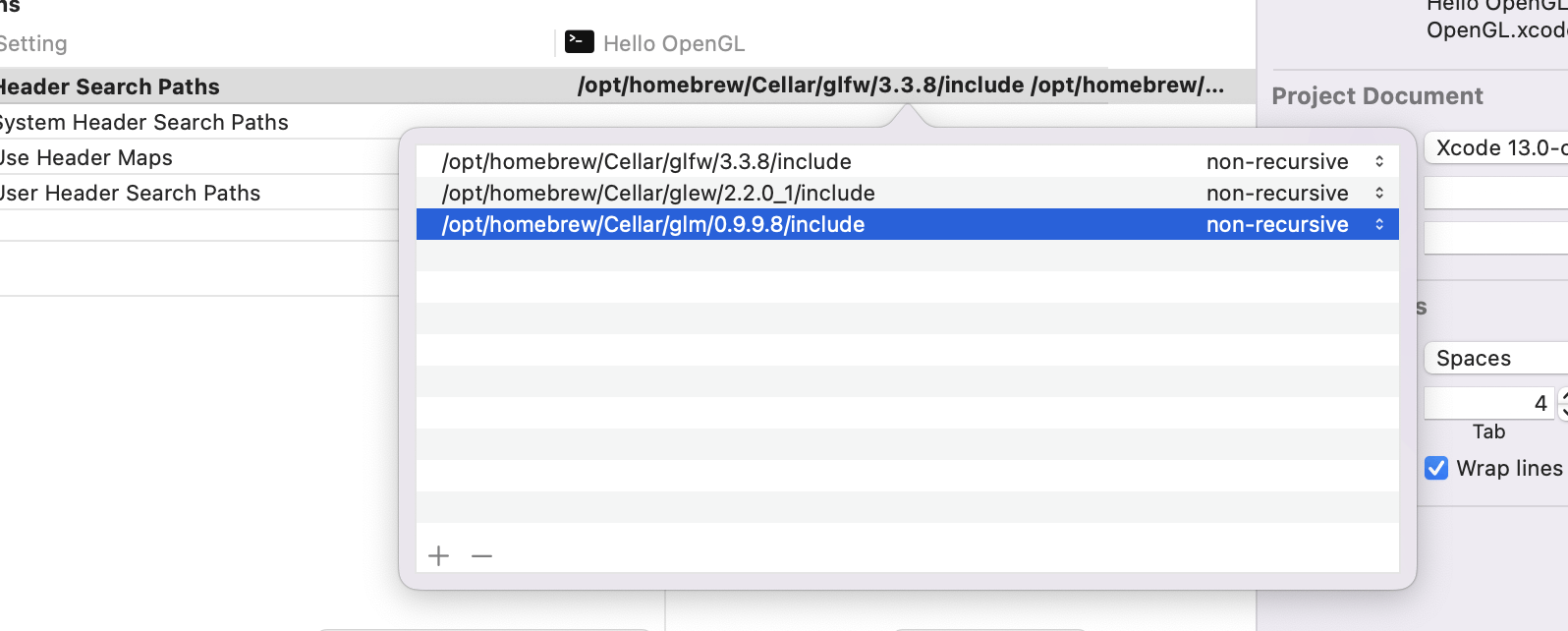
I added the glm include folder to header search
For fun I changed the code above to update the rotation applied to the triangle in the "game loop".
Program.cs