I used Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) to deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications using Kubernetes on AWS.
Since Amazon EKS is based on the open-source tool Kubernetes, applications managed by Amazon EKS are compatible with applications managed by other Kubernetes environments.
Amazon also offers the Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS).
Docker desktop
To demonstrate that I could use the same kubectl client to deploy containers to a laptop or Amazon EKS, I used this Docker Desktop example.
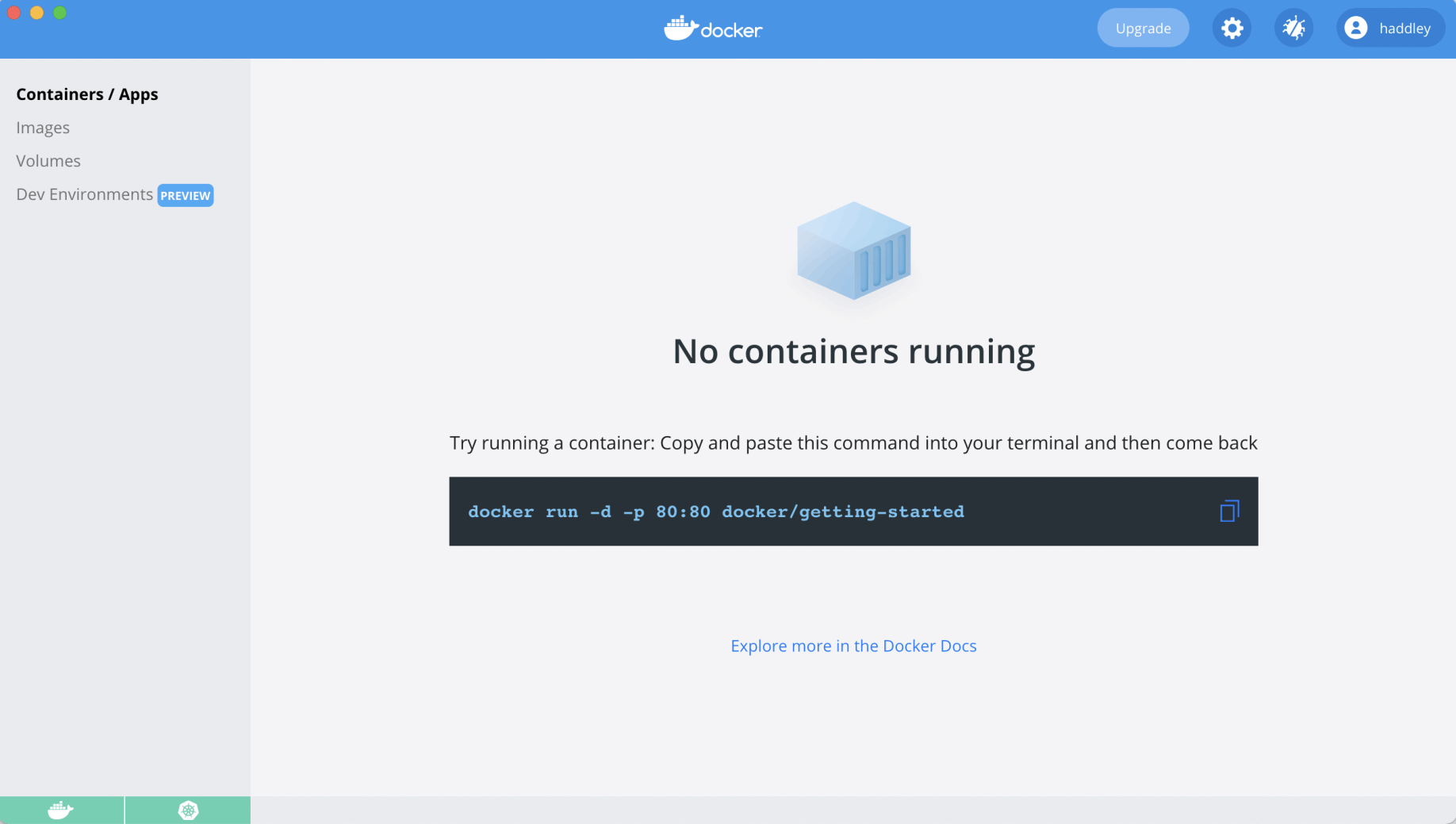
No containers were running
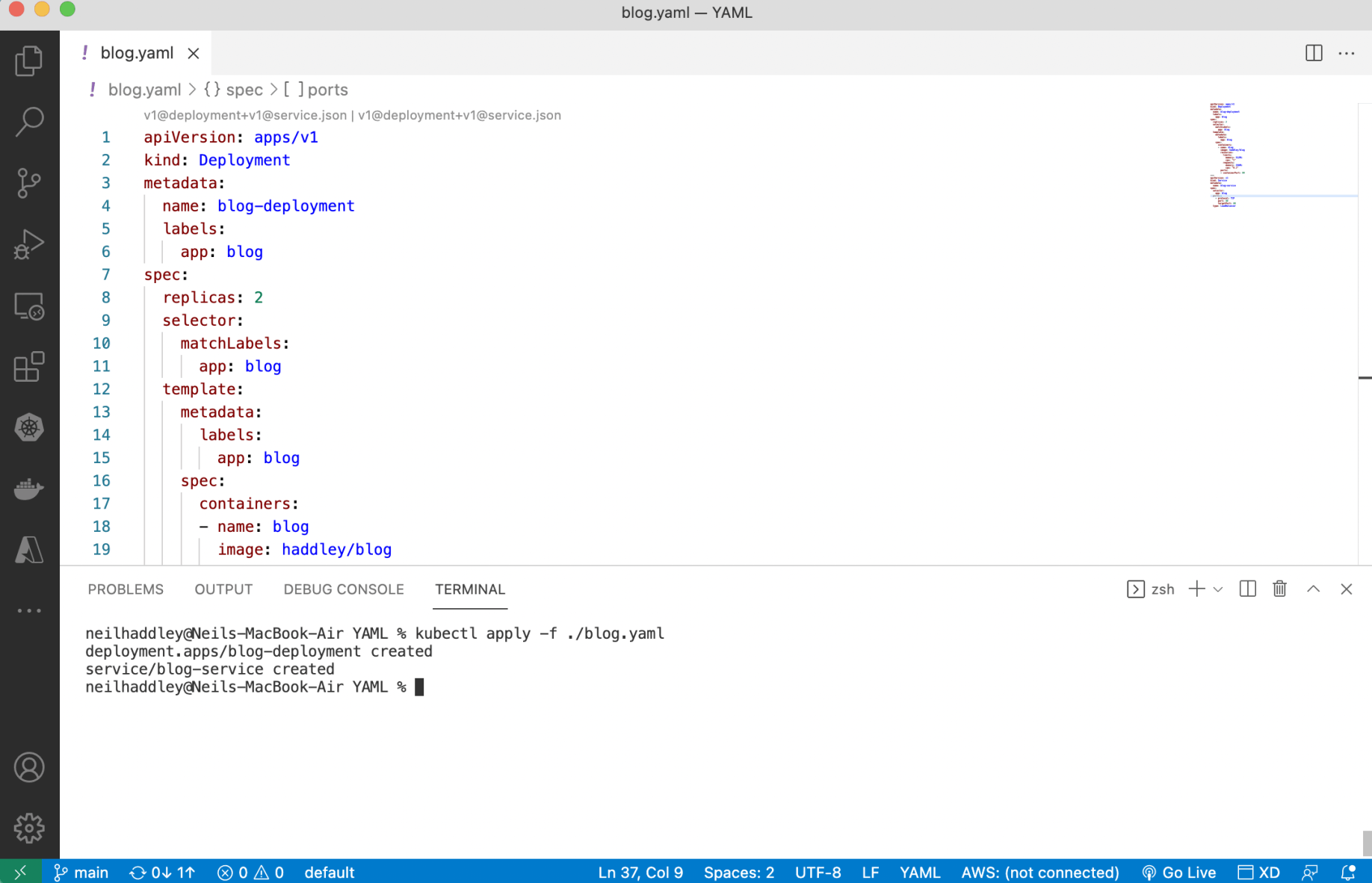
I ran kubectl apply -f ./blog.yaml
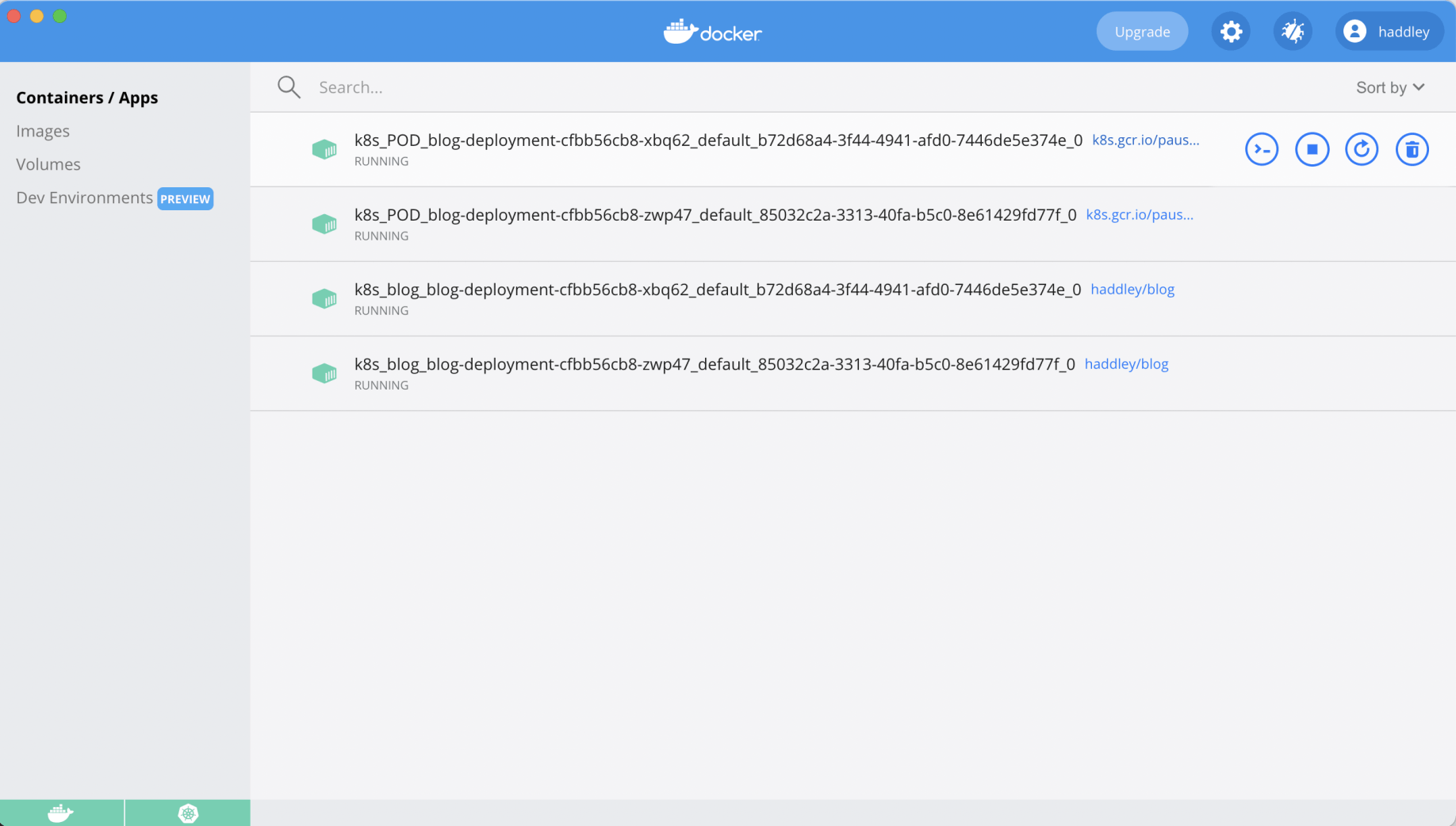
The cluster was running
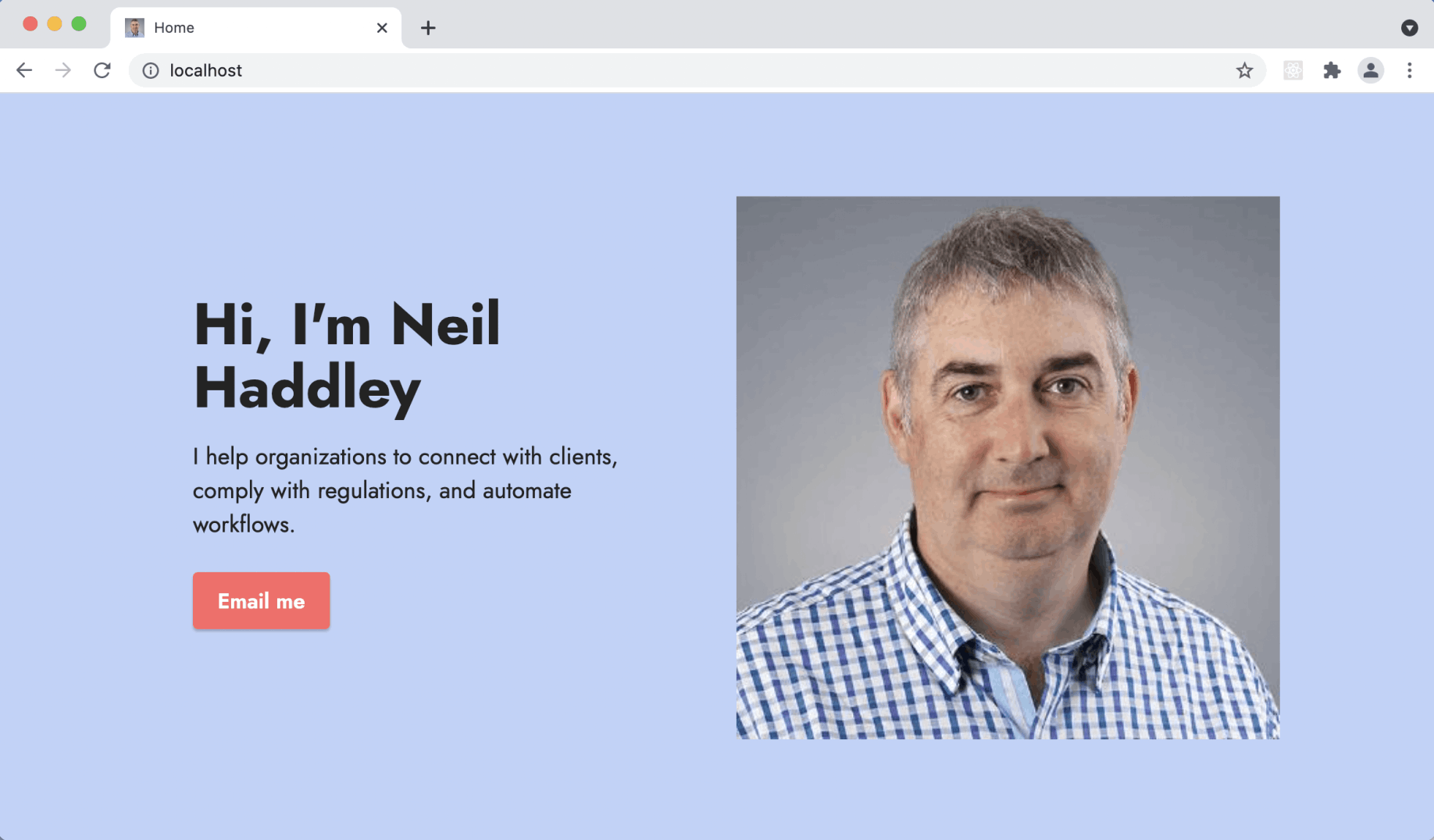
I accessed the Docker Desktop cluster
I logged in to aws.amazon.com
I navigated to the AWS Management Console
aws cli
I used the aws command line tool to manage the Amazon Web Services cloud.
I opened My Security Credentials
I created a new AWS access key
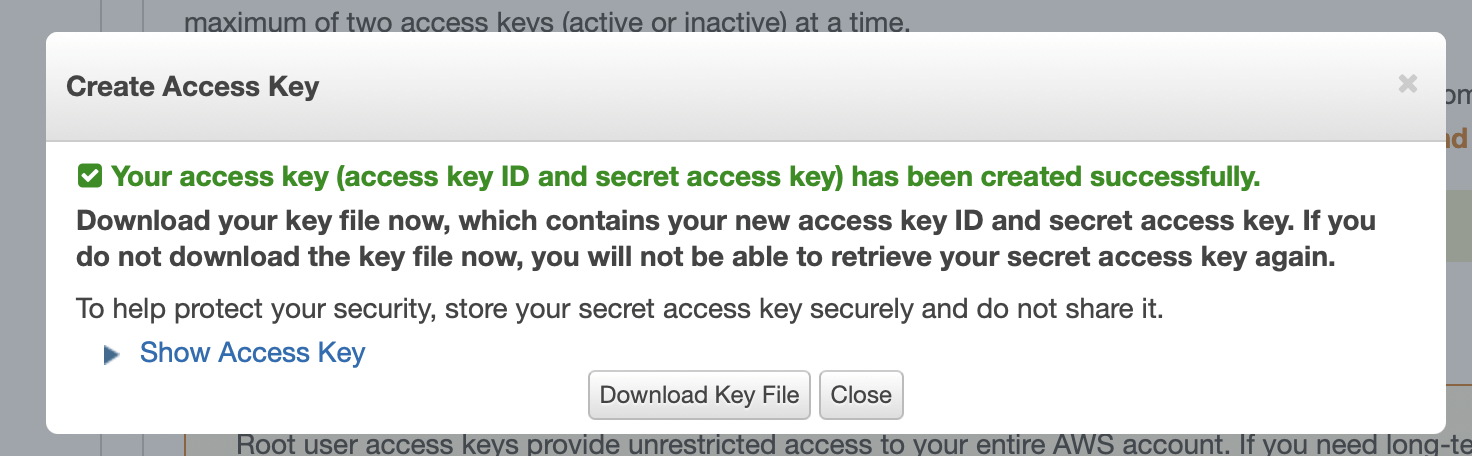
The access key was created
aws configure
I used aws configure to set credentials.
BASH
1% aws configure
AWS Access Key ID [None]: AKIAYLZDACM7MNDENQV4
AWS Secret Access Key [None]: iBXYnPPUTp+enyaVU2xvXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Default region name [None]:
Default output format [None]:
eksctl
I used eksctl, a simple CLI tool for creating clusters on Amazon EKS.
https://github.com/weaveworks/eksctl
I reviewed the eksctl documentation on the AWS site
I found the eksctl project on GitHub
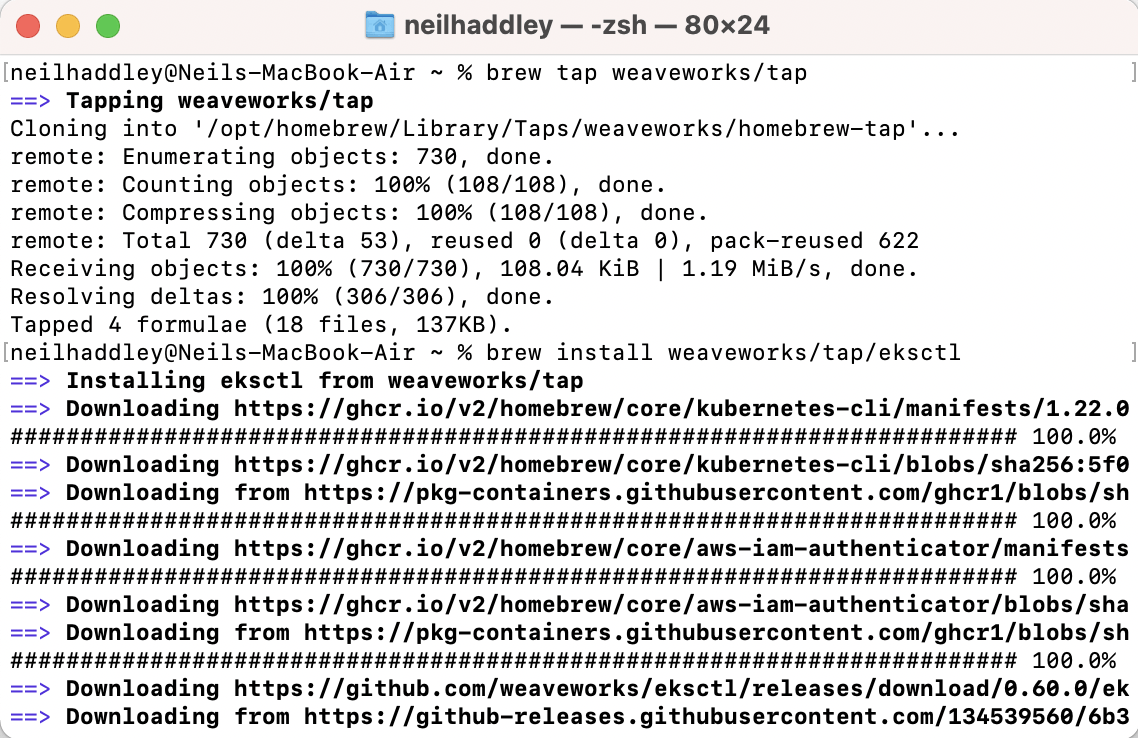
I installed eksctl
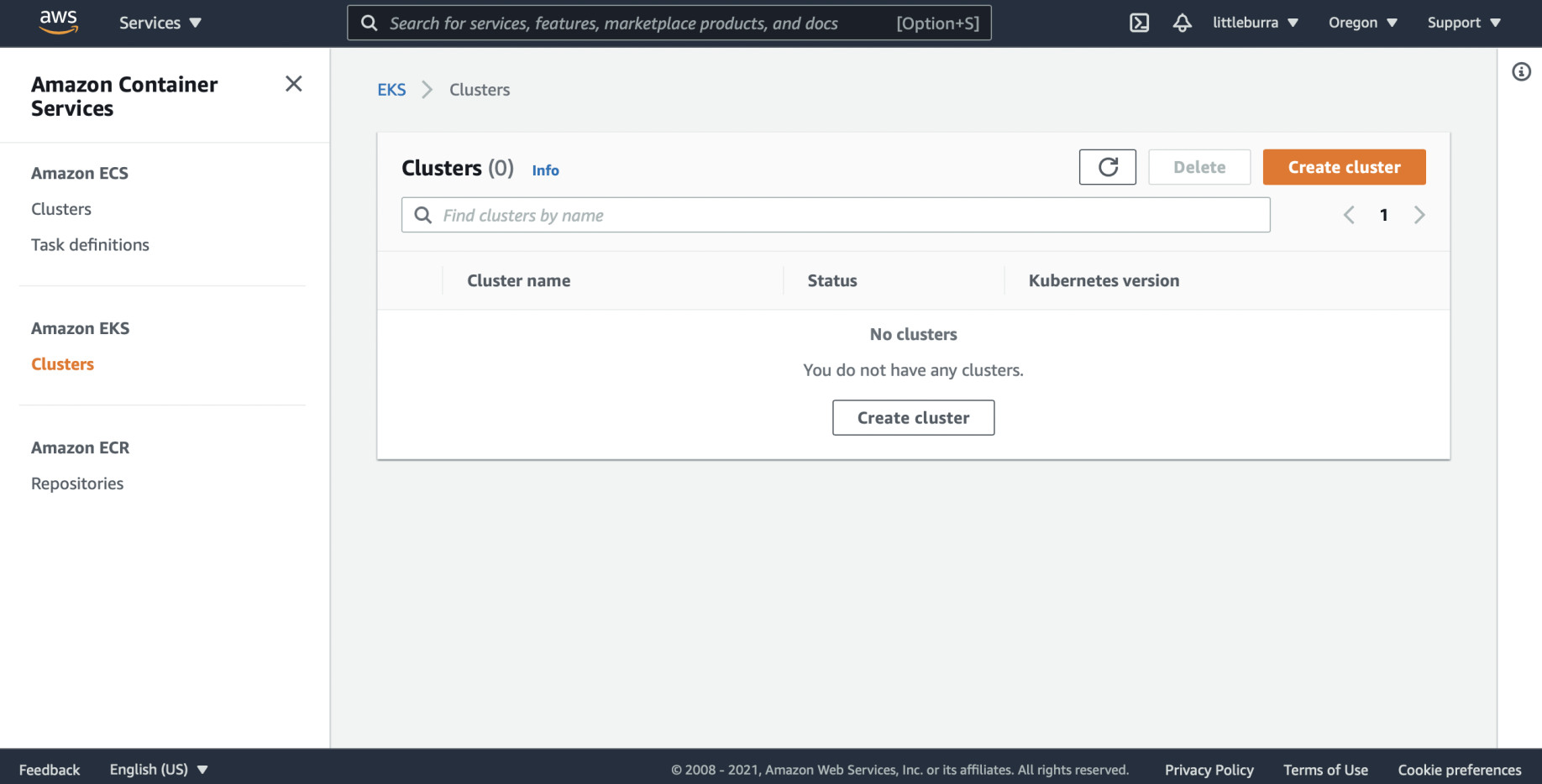
No clusters were running
eksctl create cluster
BASH
1% eksctl create cluster \ 2--name blog-cluster
Optional arguments:
BASH
1--node-type t2.nano \ 2--nodes 2
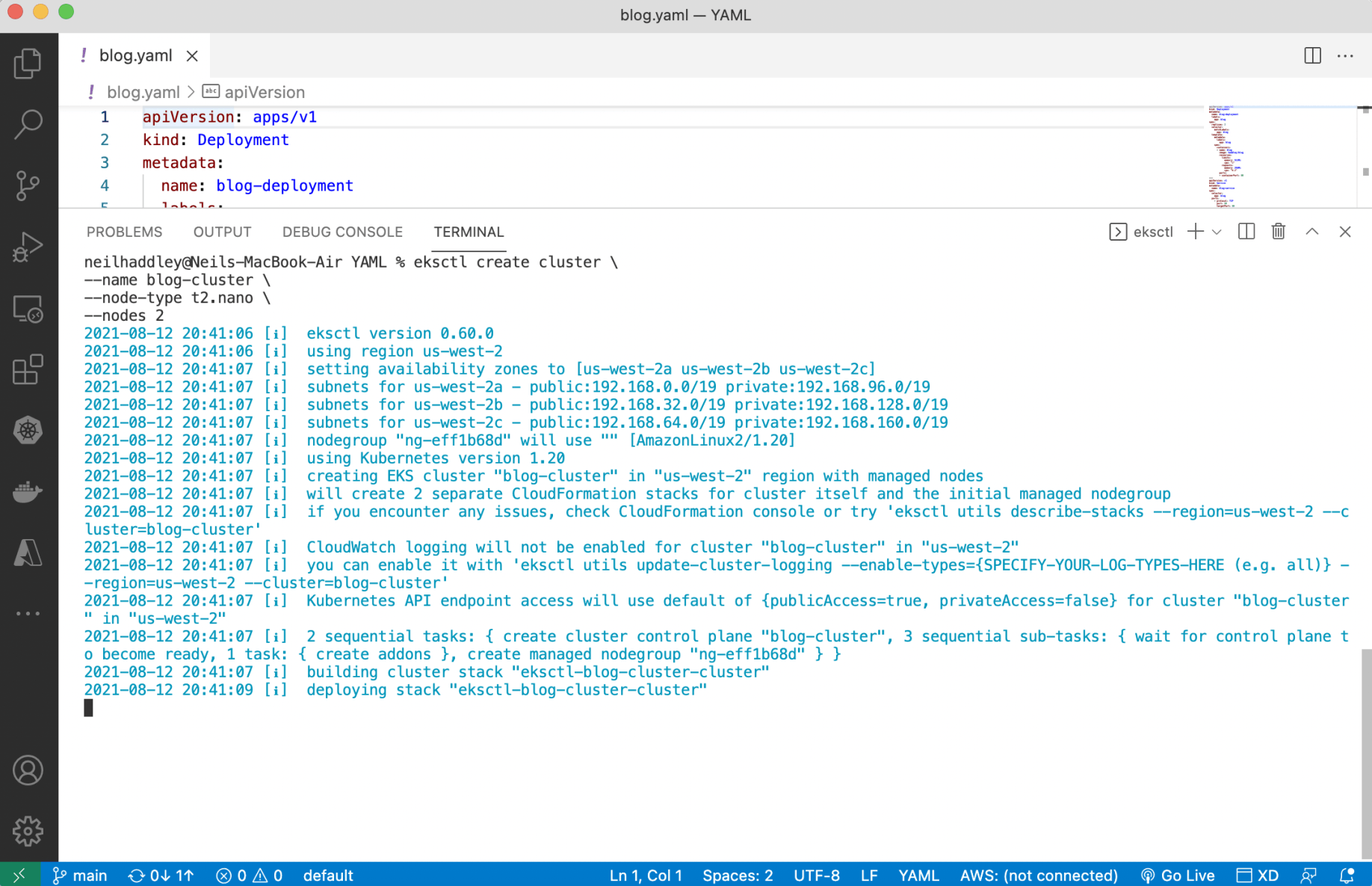
I used eksctl to create a cluster (node type t2.nano)
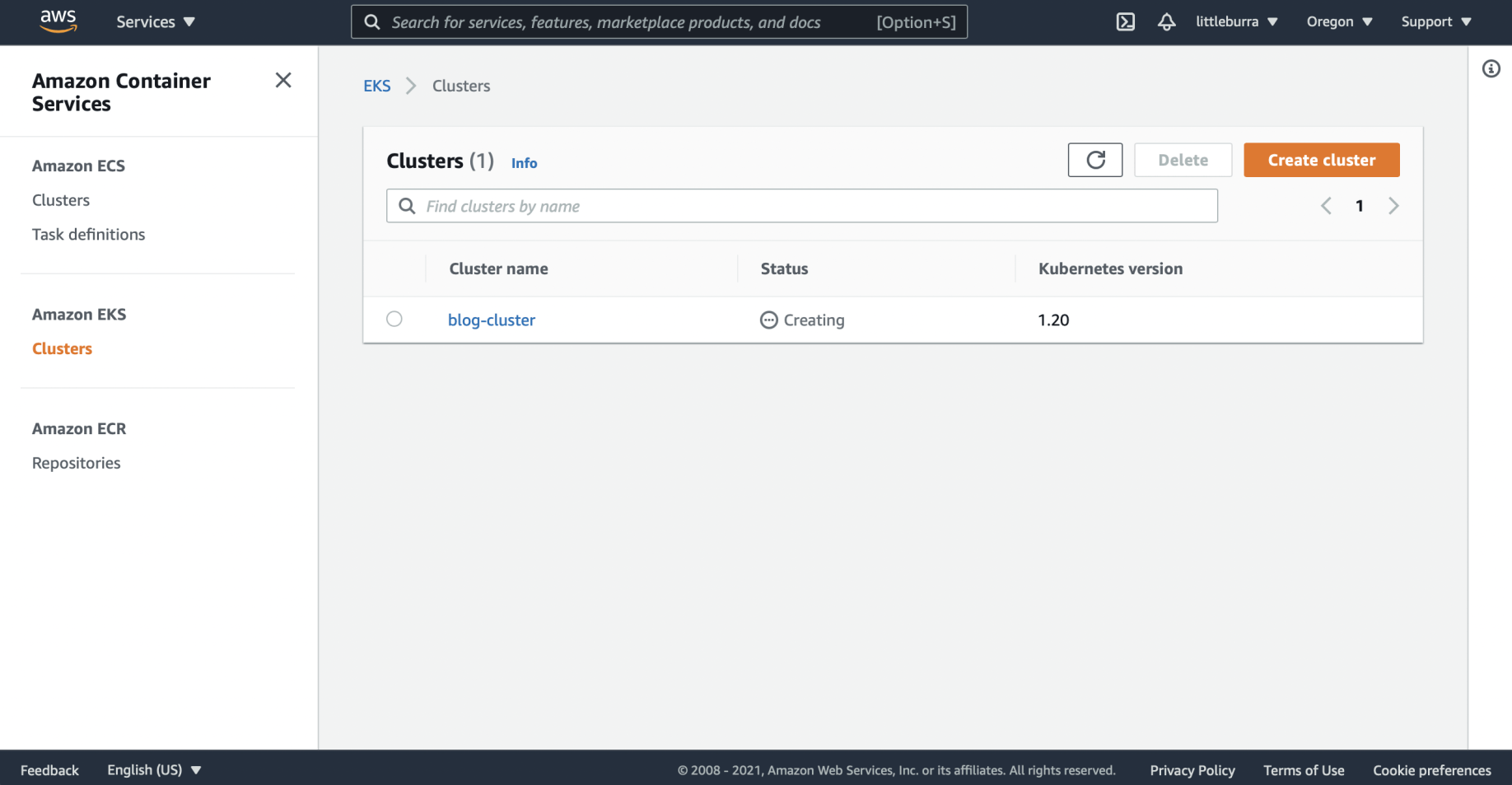
The blog-cluster was being created
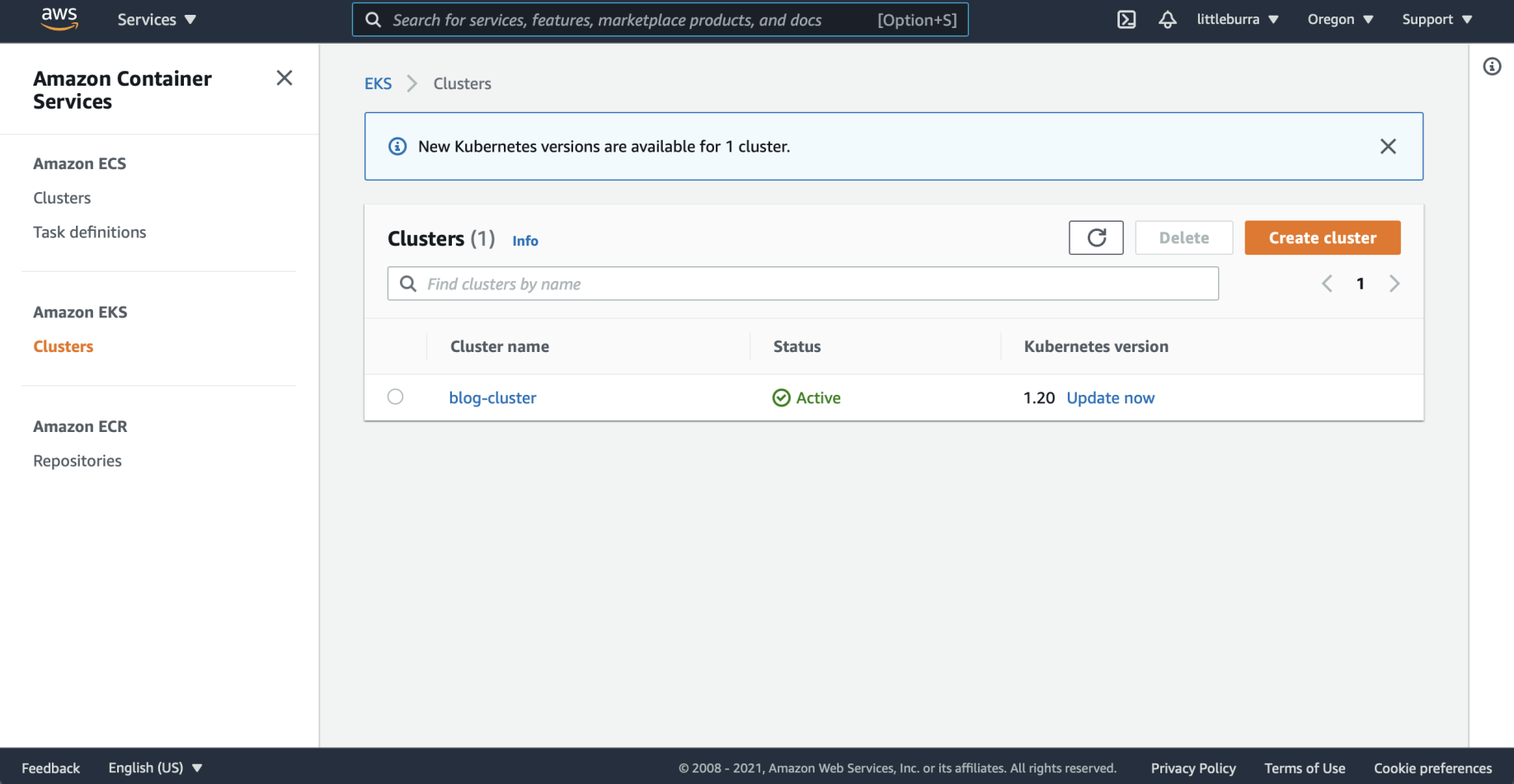
The blog-cluster was active
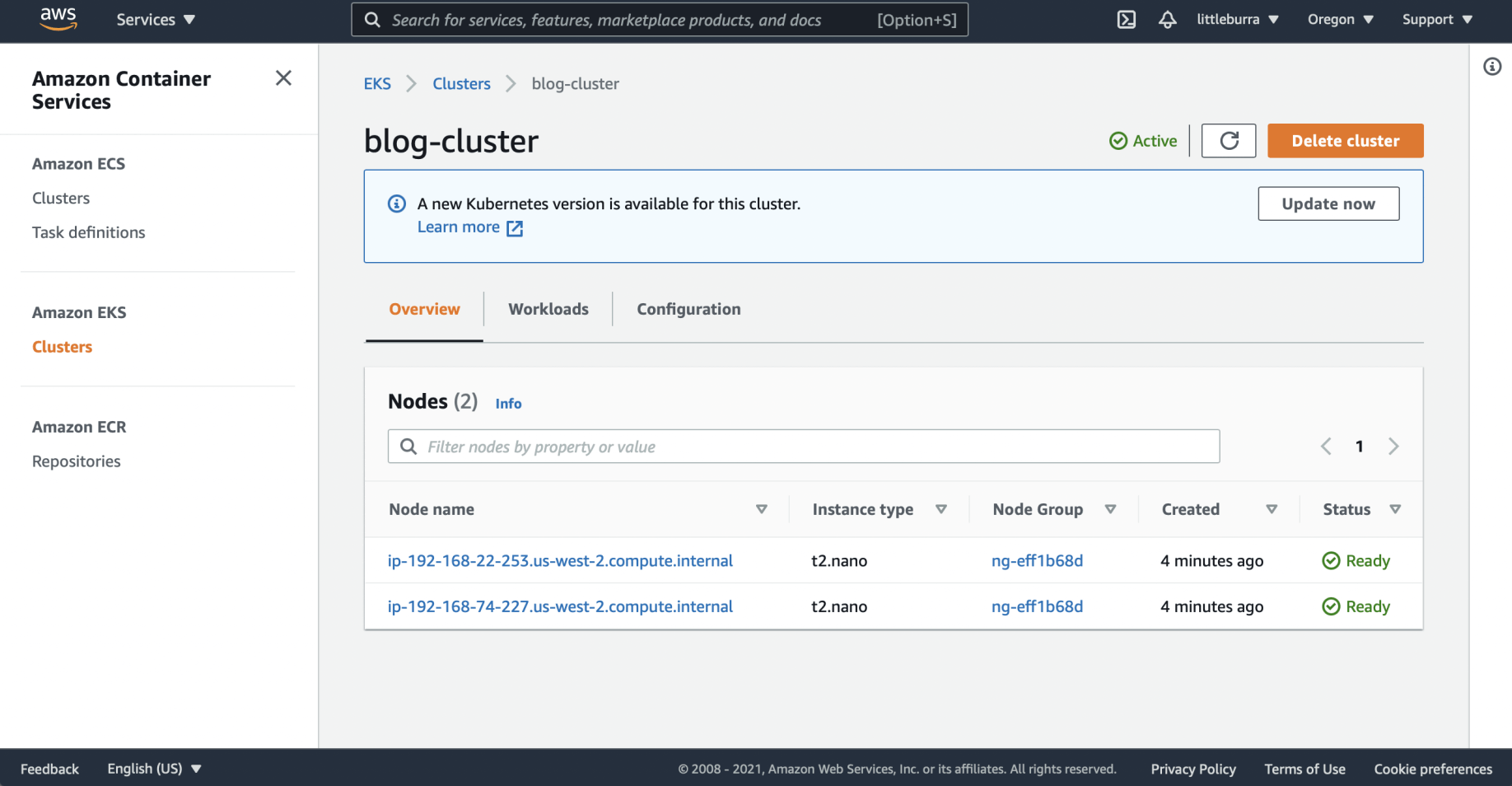
The blog-cluster EC2 nodes were created
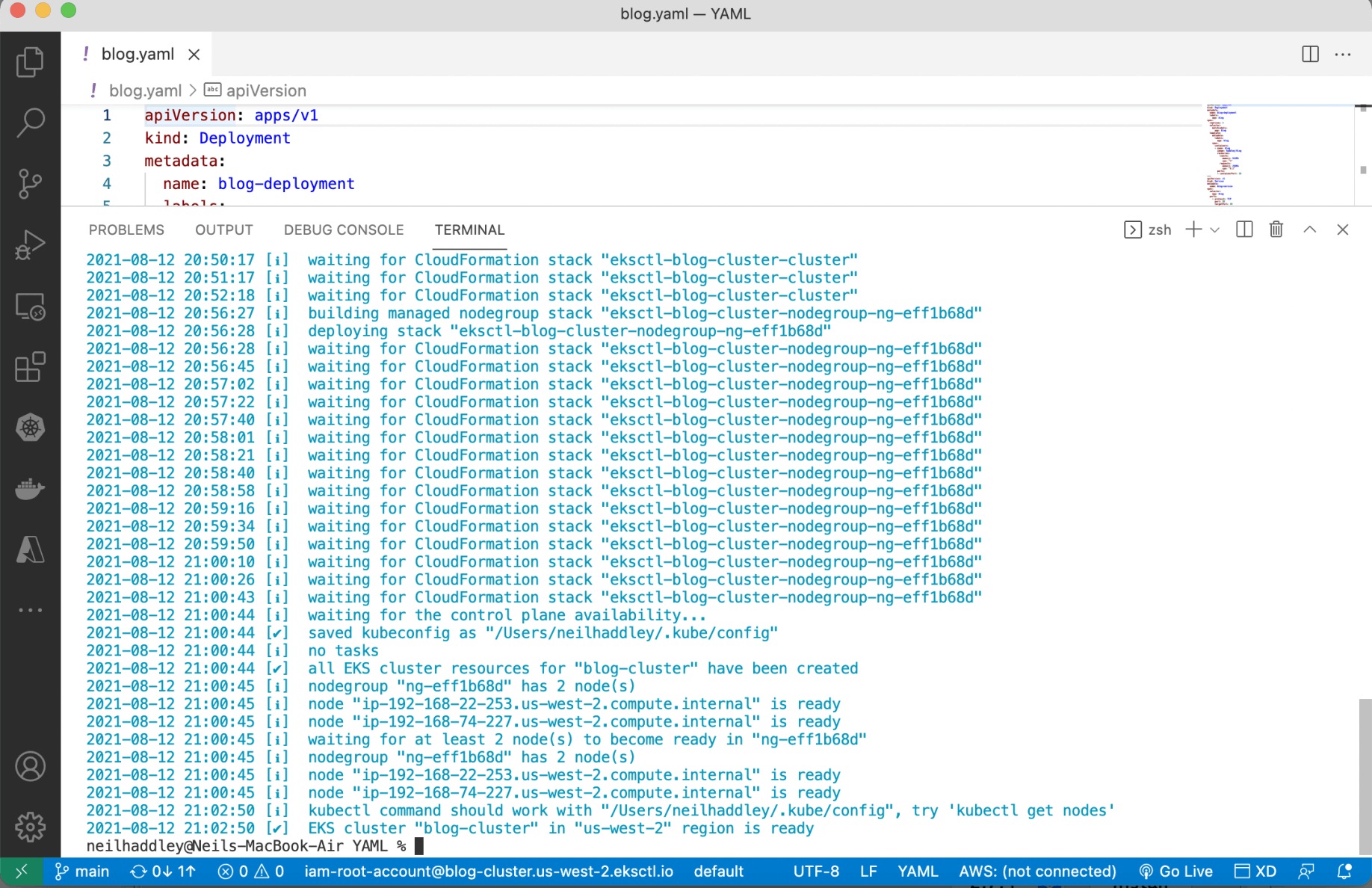
The ~/.kube/config file was updated
kubectl apply
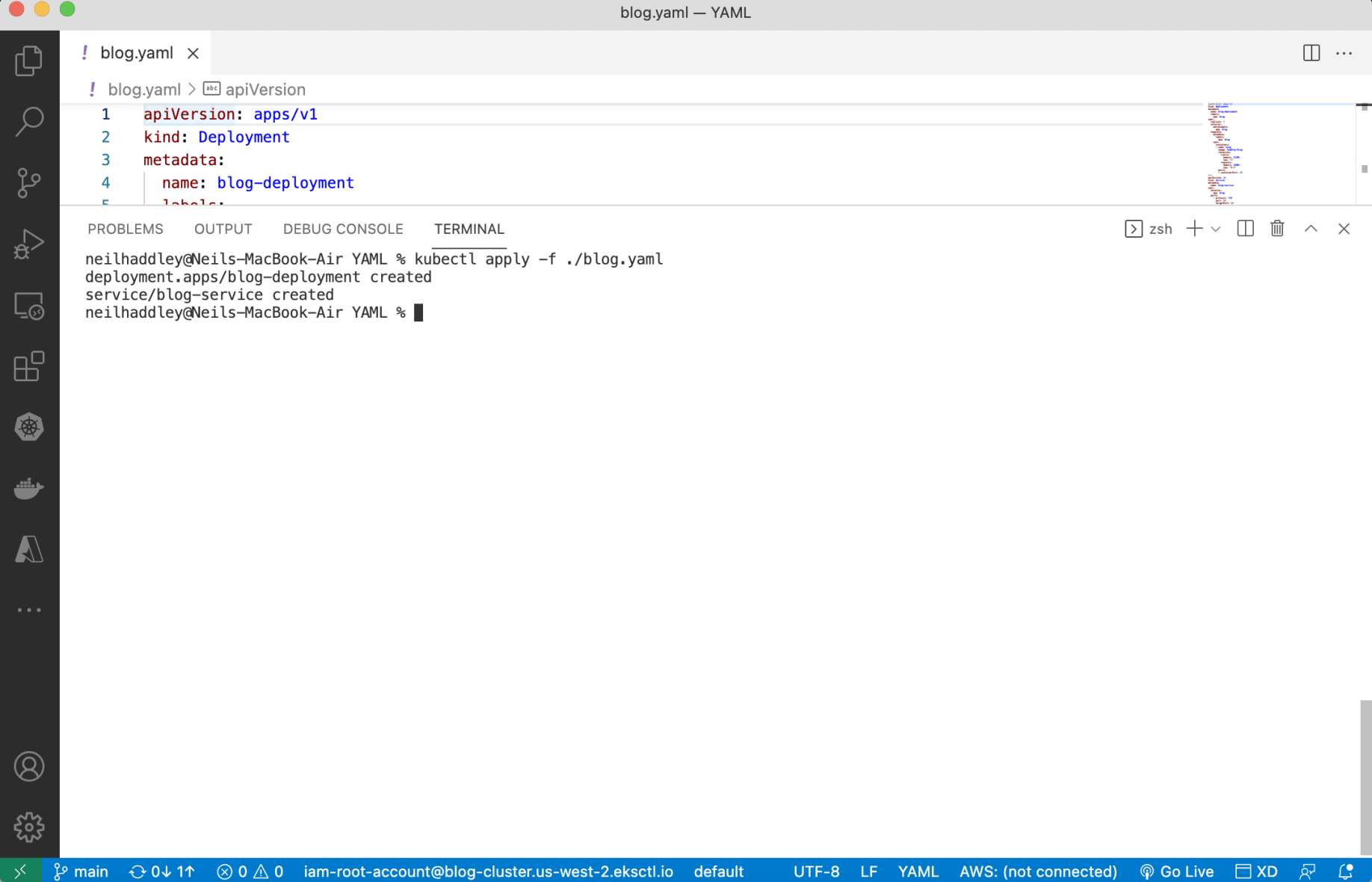
I used kubectl apply to deploy containers
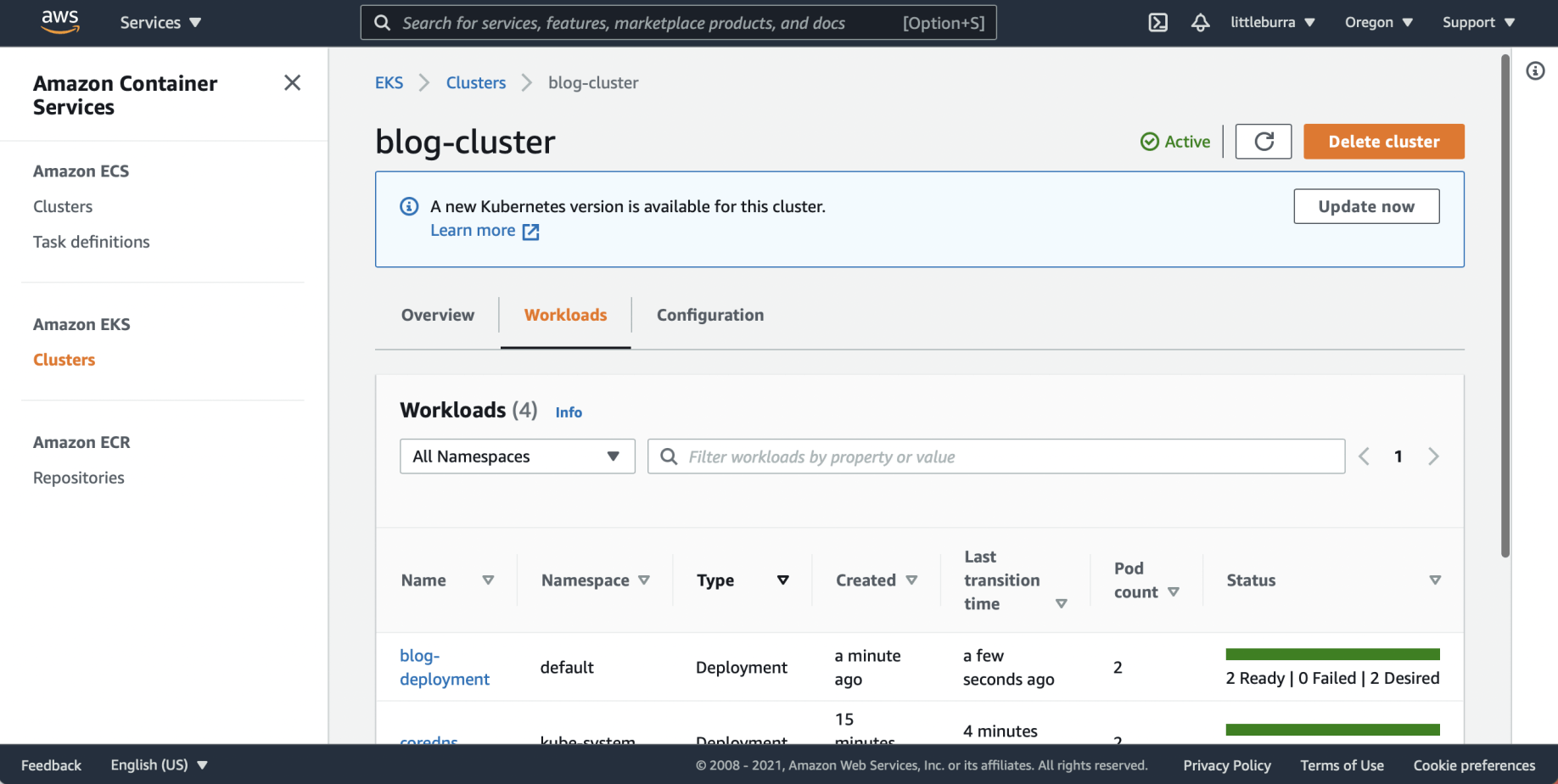
I reviewed the cluster workloads
kubectl get
I retrieved information about blog-service.
BASH
1kubectl get service/blog-service | awk {'print $1" " $2 " " $4 " " $5'} | column -t
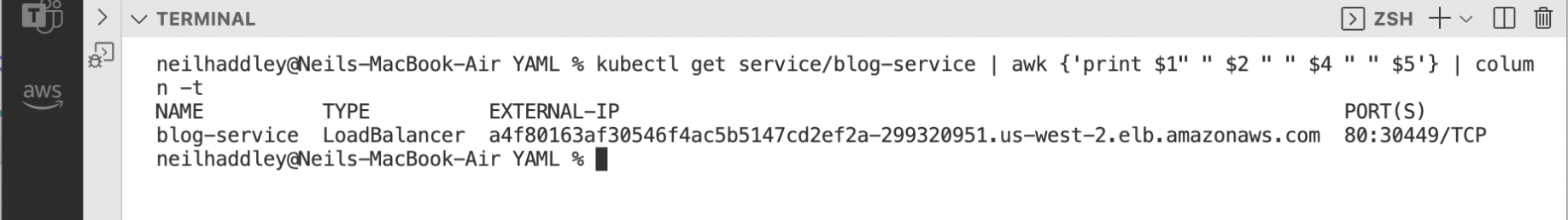
I retrieved the load balancer URL
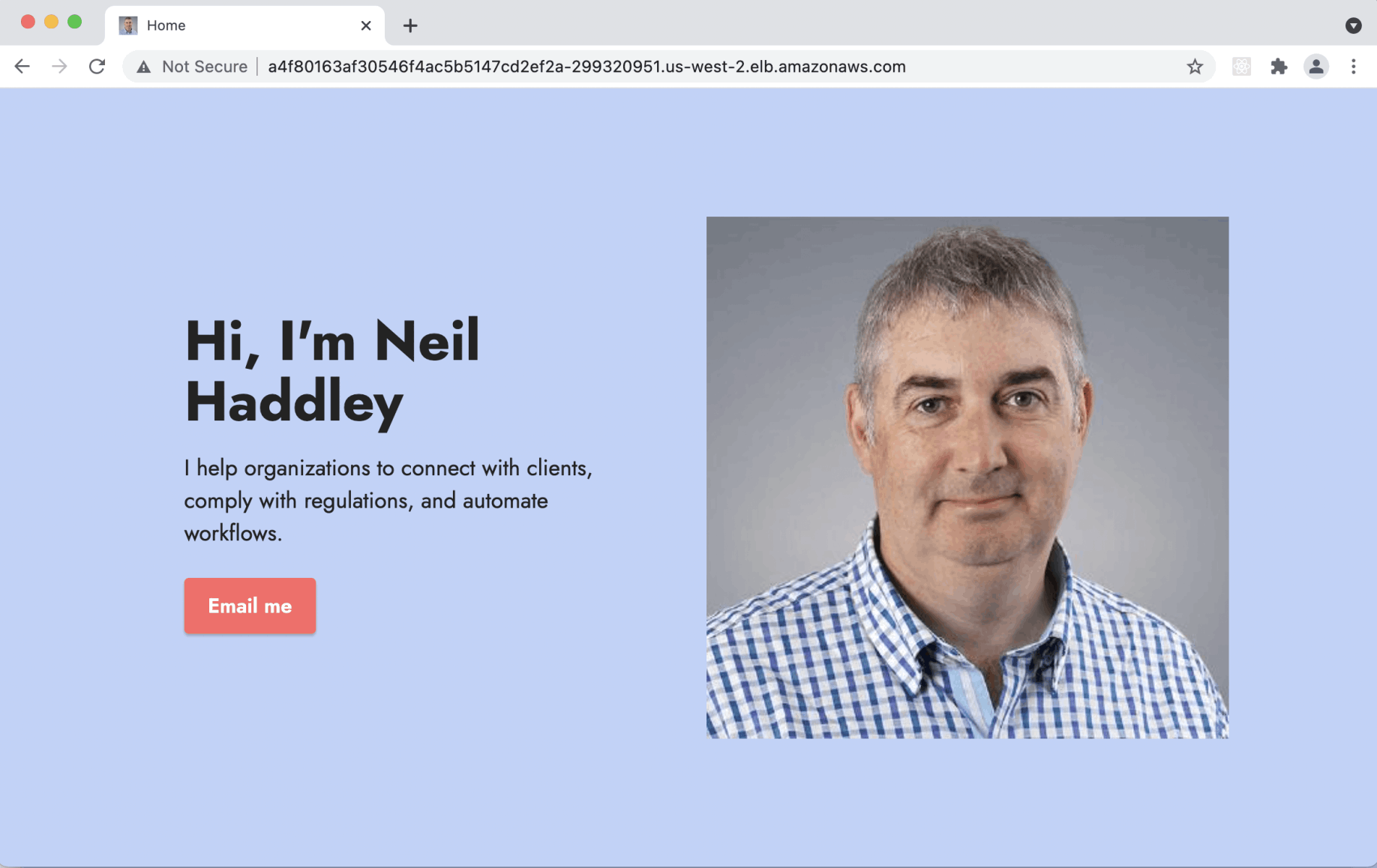
I accessed the Amazon EKS cluster
eksctl delete cluster
I used eksctl delete to remove the cluster.
BASH
1% eksctl delete cluster \ 2 --name blog-cluster
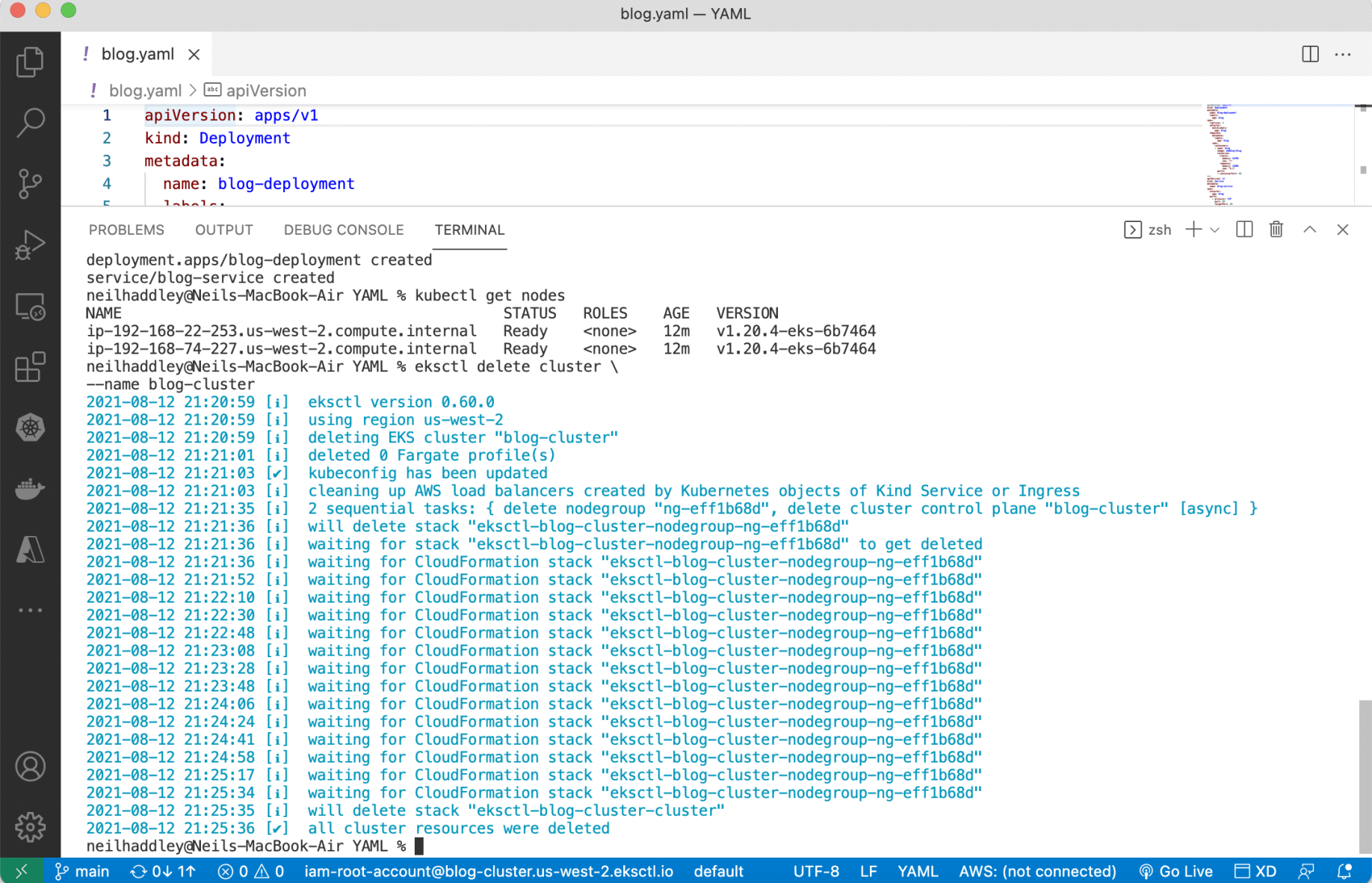
I ran eksctl delete cluster
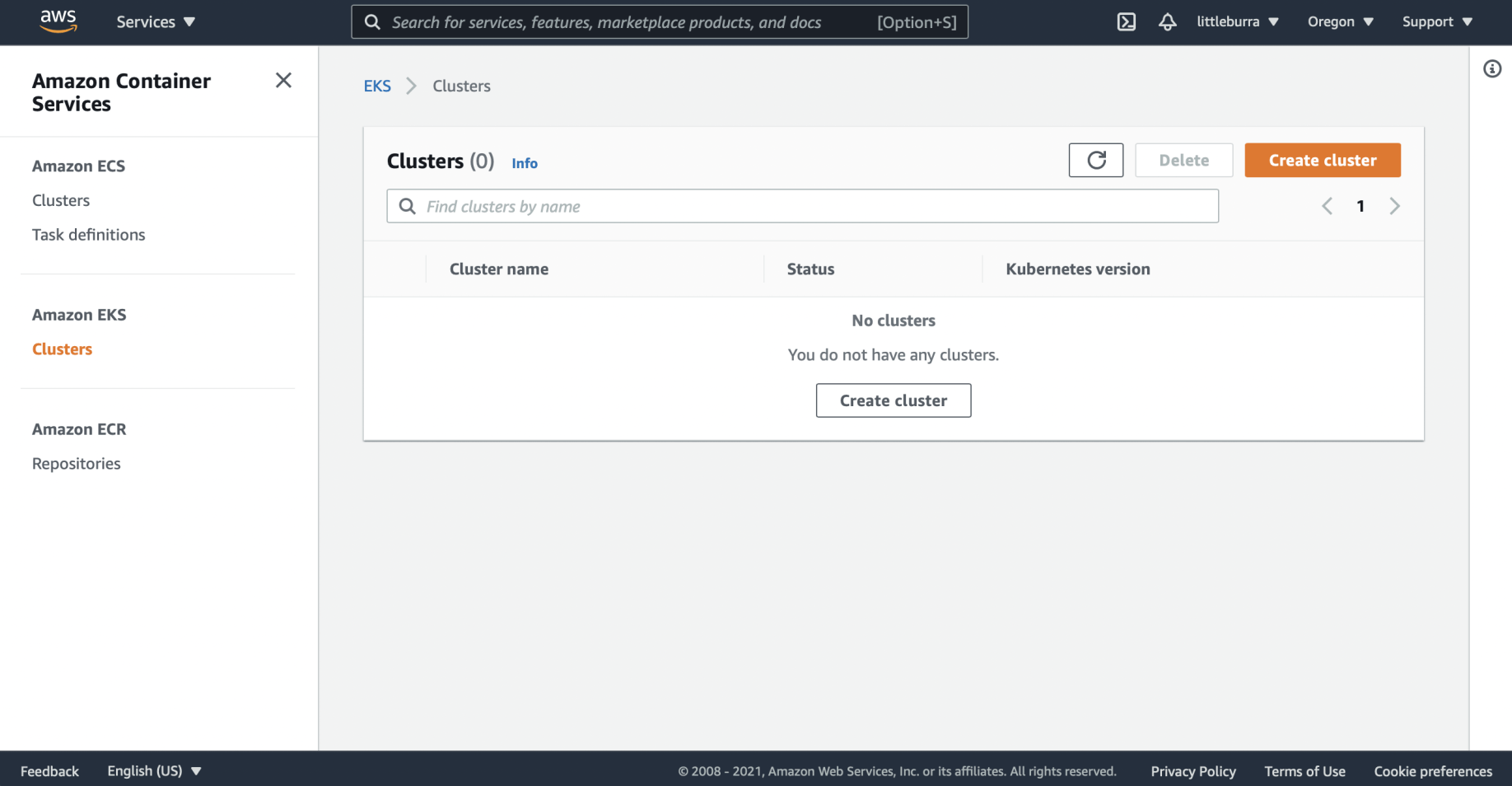
The cluster was deleted
kubectl config use-context
I switched back to using Docker Desktop.
BASH
1% kubectl config use-context docker-desktop
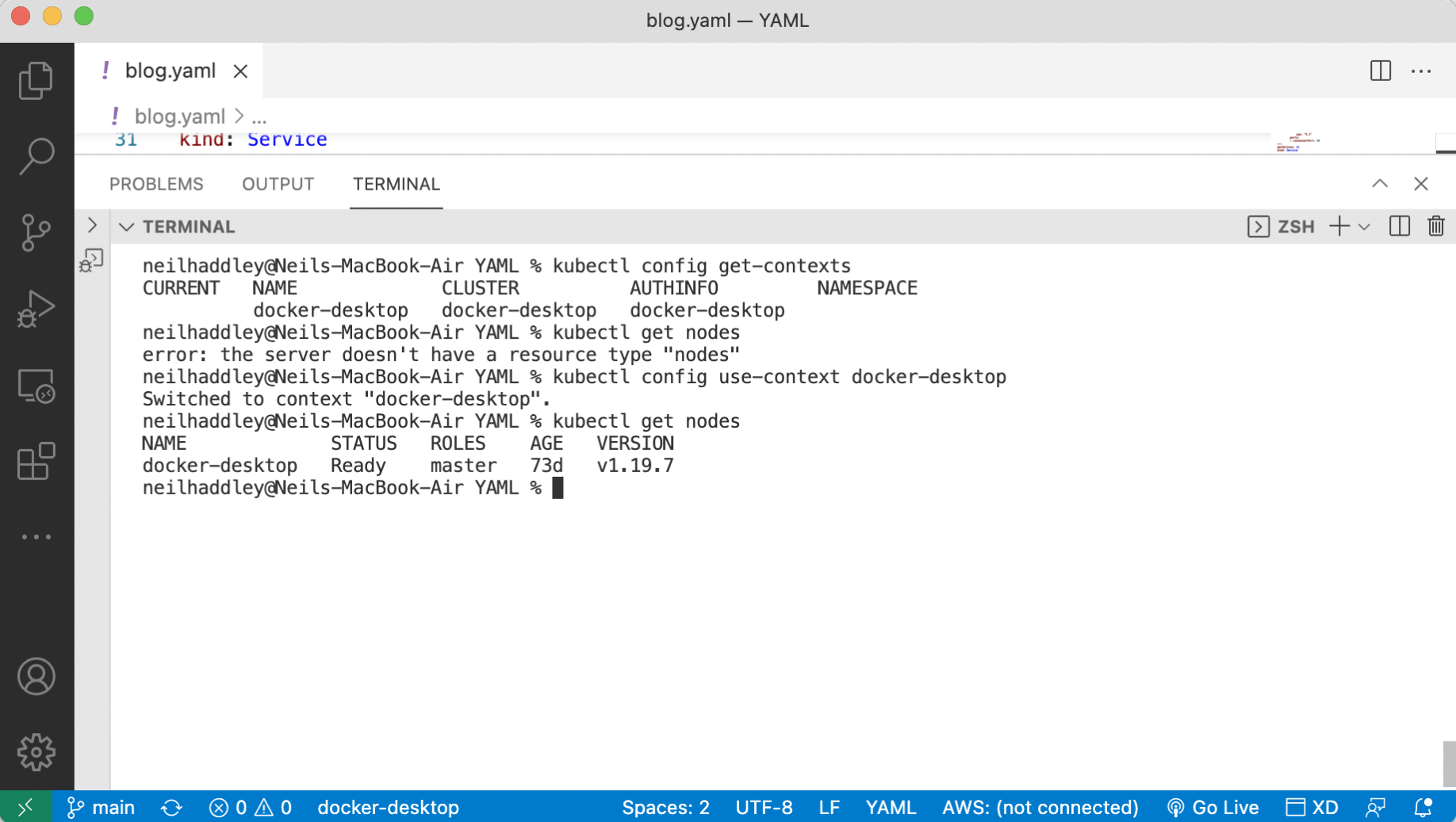
I switched back to docker-desktop
Deleting an AWS Access Key
Publishing AWS access keys is not a great idea, so I deleted mine.
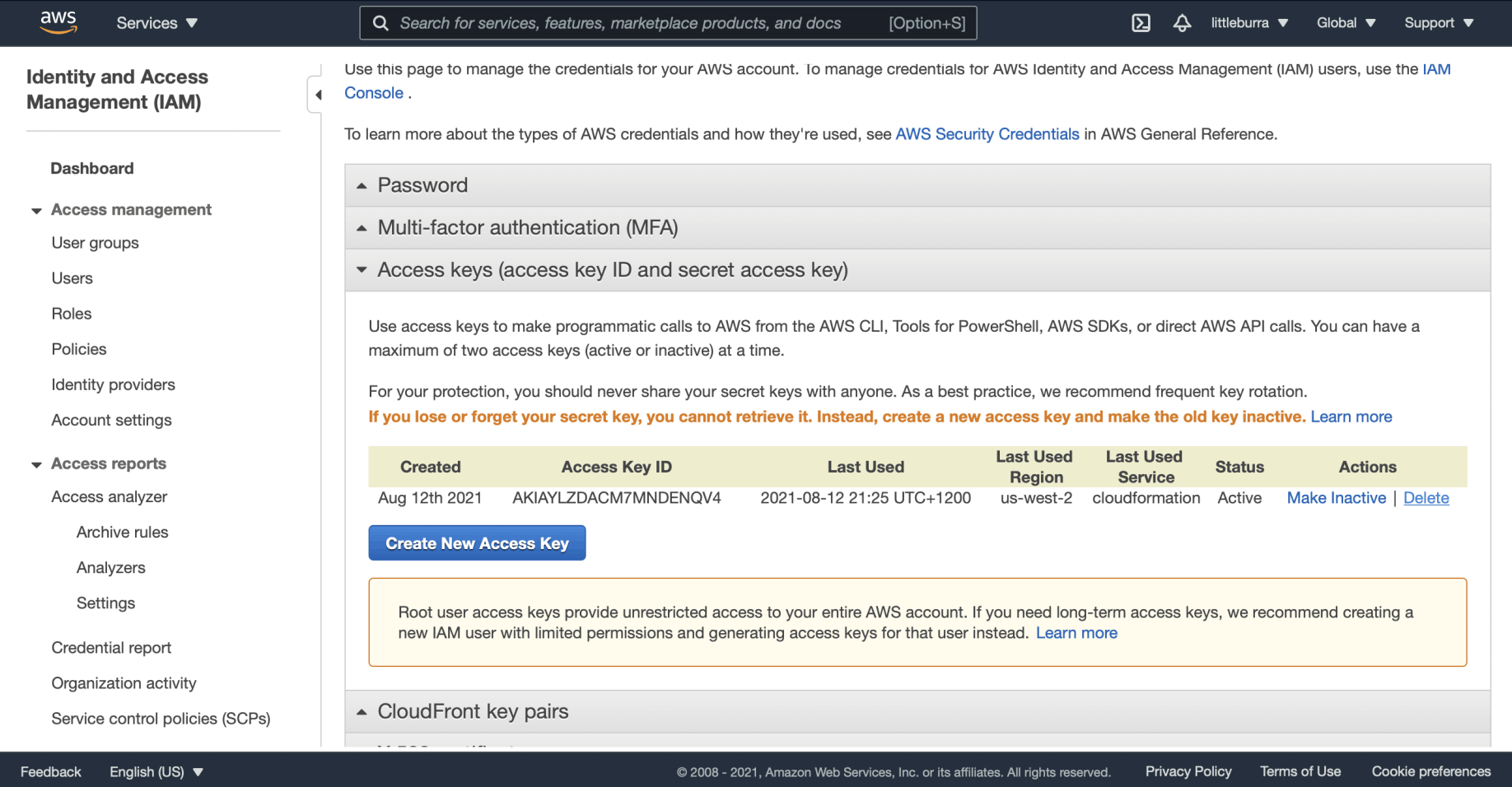
I selected the Delete link
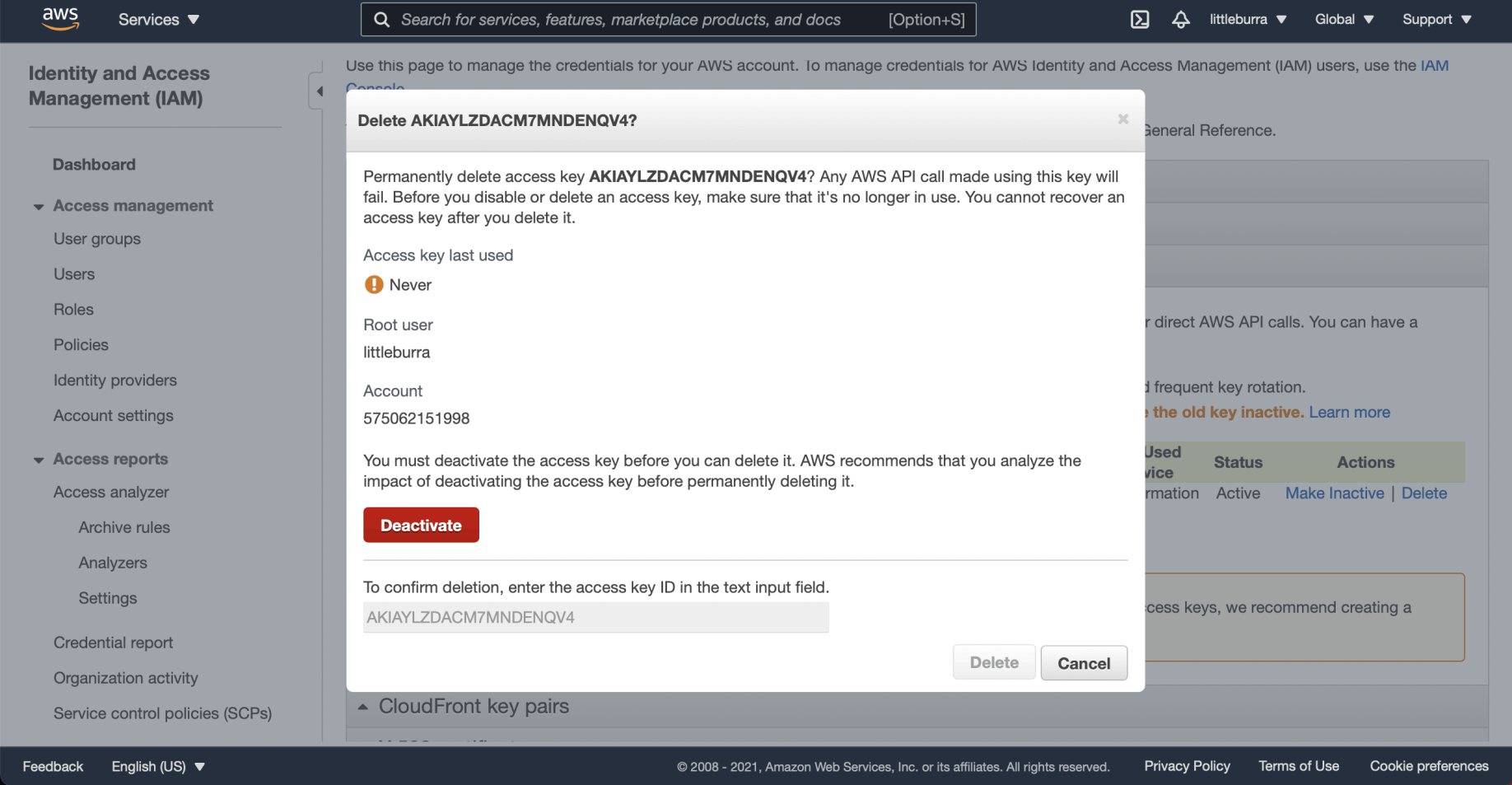
I clicked the Deactivate button
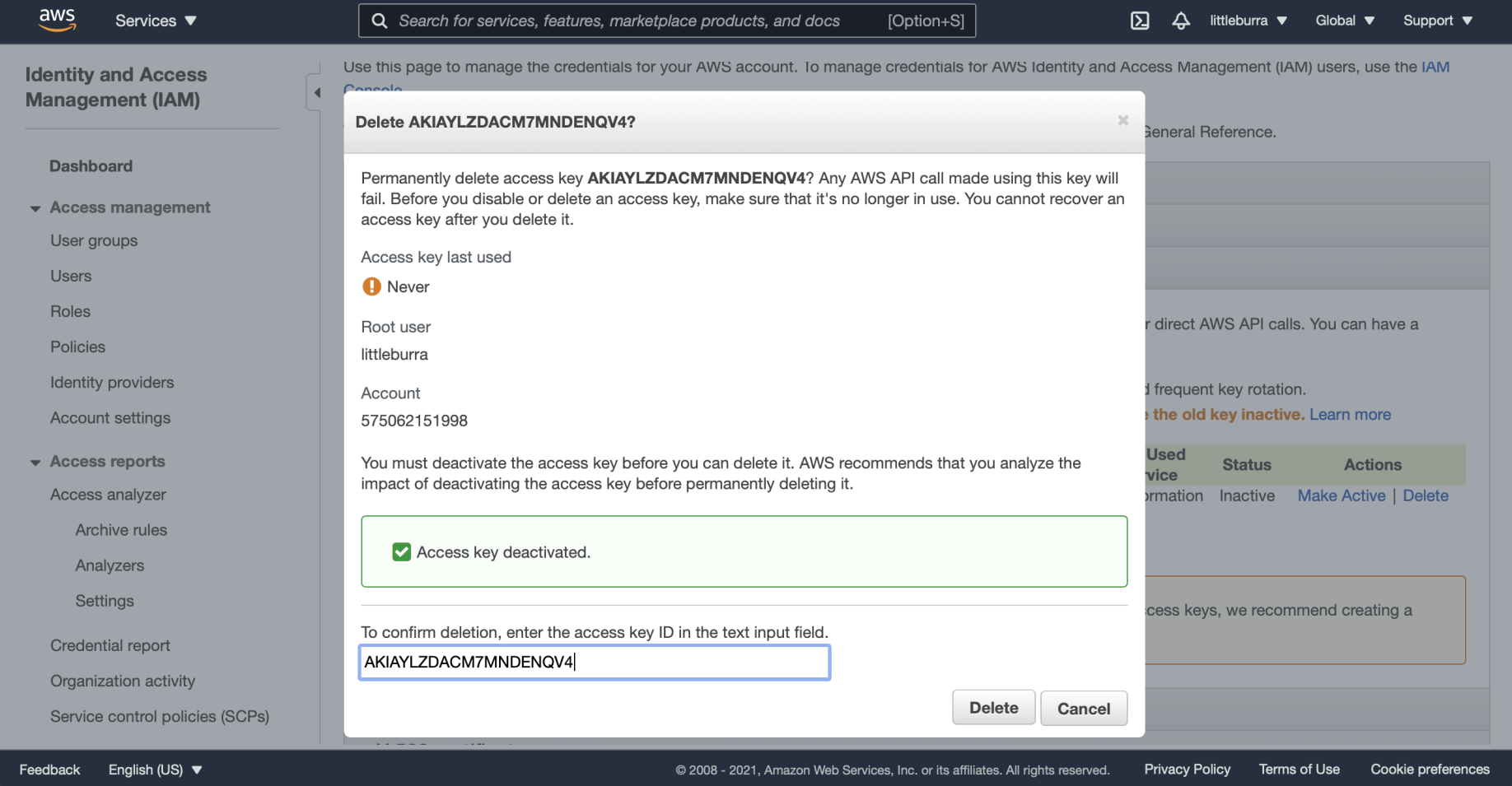
I confirmed the access key name and clicked Delete
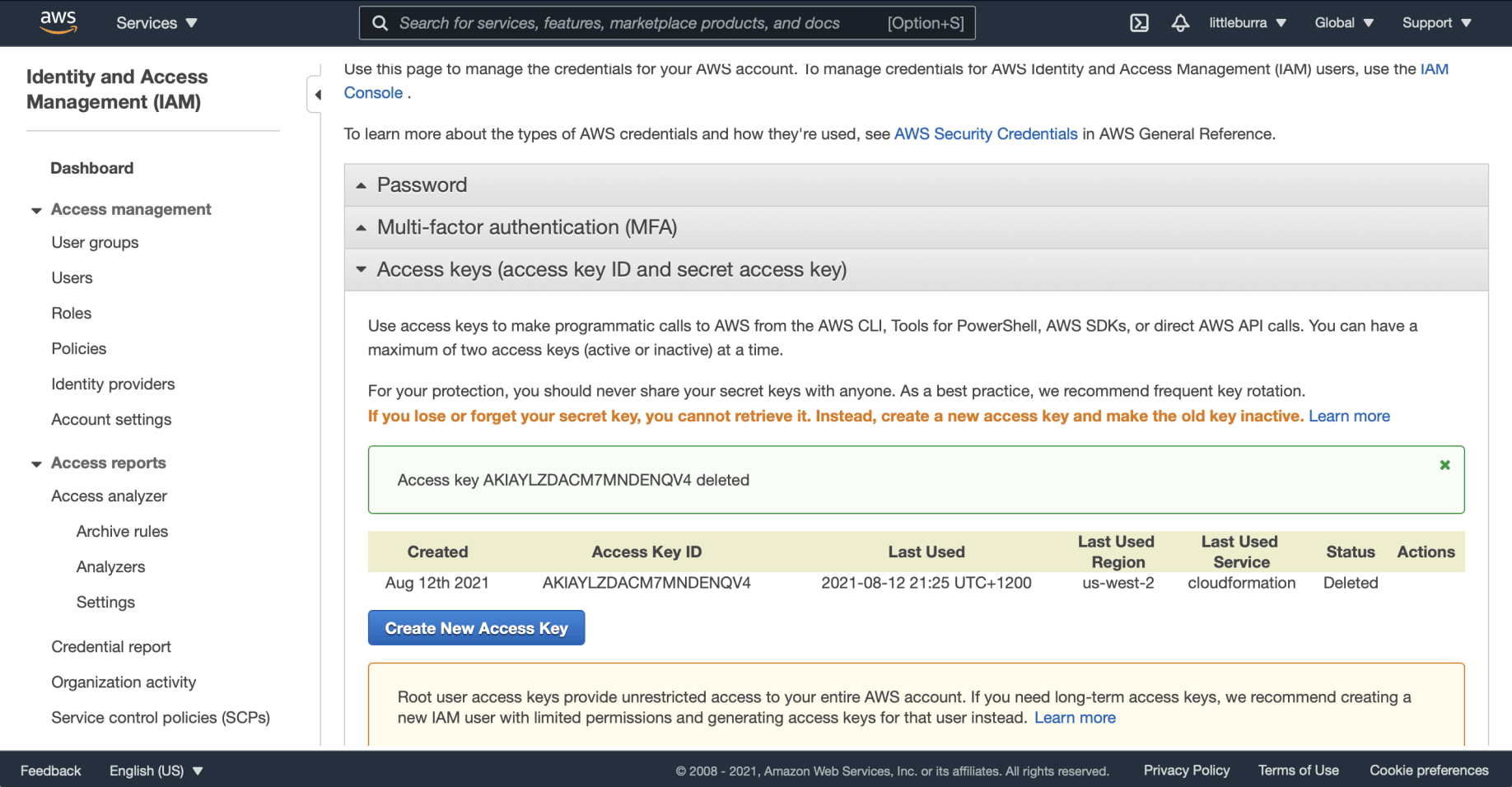
The access key was deleted